Page 156 - Design of Solar Thermal Power Plants
P. 156
3.2 HELIOSTAT FIELD EFFICIENCY ANALYSIS 141
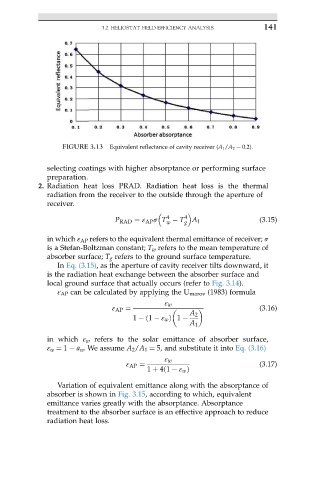
FIGURE 3.13 Equivalent reflectance of cavity receiver (A 1 /A 2 ¼ 0.2).
selecting coatings with higher absorptance or performing surface
preparation.
2. Radiation heat loss PRAD. Radiation heat loss is the thermal
radiation from the receiver to the outside through the aperture of
receiver.
4
P RAD ¼ ε AP s T T 4 g A 1 (3.15)
w
in which ε AP refers to the equivalent thermal emittance of receiver; s
is a Stefan-Boltzman constant; T w refers to the mean temperature of
absorber surface; T g refers to the ground surface temperature.
In Eq. (3.15), as the aperture of cavity receiver tilts downward, it
is the radiation heat exchange between the absorber surface and
local ground surface that actually occurs (refer to Fig. 3.14).
ε AP can be calculated by applying the U marov (1983) formula
ε w
ε AP ¼ (3.16)
A 2
1 ð1 ε w Þ 1
A 1
in which ε w refers to the solar emittance of absorber surface,
ε w ¼ 1 a w . We assume A 2 /A 1 ¼ 5, and substitute it into Eq. (3.16)
ε w
ε AP ¼ (3.17)
1 þ 4ð1 ε w Þ
Variation of equivalent emittance along with the absorptance of
absorber is shown in Fig. 3.15, according to which, equivalent
emittance varies greatly with the absorptance. Absorptance
treatment to the absorber surface is an effective approach to reduce
radiation heat loss.