Page 138 - Designing Sociable Robots
P. 138
breazeal-79017 book March 18, 2002 14:5
The Motivation System 119
Drives over- Emotion
Elicitors
whelming Sorrow Disgust
V, S
V,S
high arousal,
Releasers Anger
Affective negative Surprise
Assessment valence, A, S Boredom A,V
Big S
closed stance Calm
Threat S
Close Threat
SM
Fear Joy Interest
Fast A,V,S A A,S
Motion
success,
frustration
Emotion
Arbitration
Behavior Sorrow Boredom
System Interest Calm
Flee Fear
Behavior
Surprise Joy Disgust Anger
Motor net arousal, valence, stance
Systems
Escape
Motor Express Express Express
Skill Voice Face Posture
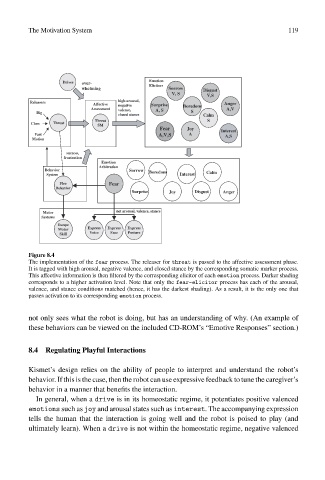
Figure 8.4
The implementation of the fear process. The releaser for threat is passed to the affective assessment phase.
It is tagged with high arousal, negative valence, and closed stance by the corresponding somatic marker process.
This affective information is then filtered by the corresponding elicitor of each emotion process. Darker shading
corresponds to a higher activation level. Note that only the fear-elicitor process has each of the arousal,
valence, and stance conditions matched (hence, it has the darkest shading). As a result, it is the only one that
passes activation to its corresponding emotion process.
not only sees what the robot is doing, but has an understanding of why. (An example of
these behaviors can be viewed on the included CD-ROM’s “Emotive Responses” section.)
8.4 Regulating Playful Interactions
Kismet’s design relies on the ability of people to interpret and understand the robot’s
behavior. If this is the case, then the robot can use expressive feedback to tune the caregiver’s
behavior in a manner that benefits the interaction.
In general, when a drive is in its homeostatic regime, it potentiates positive valenced
emotions such as joy and arousal states such as interest. The accompanying expression
tells the human that the interaction is going well and the robot is poised to play (and
ultimately learn). When a drive is not within the homeostatic regime, negative valenced