Page 170 - Designing Sociable Robots
P. 170
breazeal-79017 book March 18, 2002 14:7
The Behavior System 151
Avoidance Behavior
2000
Activation Level 1000 0 Stimulation Drive
–1000
Engage Toy Behavior
Avoid Toy Behavior
–2000 Seek Toy Behavior
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Time (seconds)
2000
Activation Level 0 Interest
1000
–1000
Displeasure
Fear
–2000 Sadness
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Time (seconds)
1
Position (% of Total Range) 0.5 0
0.5
Eye Pan
Eye Tilt
Neck Pan
1
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Time (seconds)
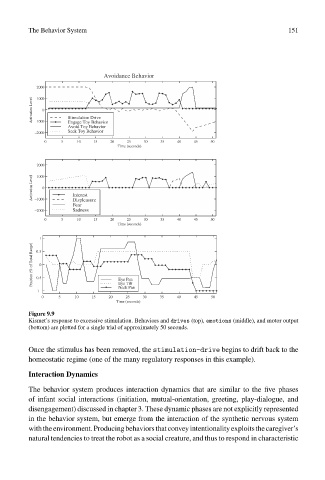
Figure 9.9
Kismet’s response to excessive stimulation. Behaviors and drives (top), emotions (middle), and motor output
(bottom) are plotted for a single trial of approximately 50 seconds.
Once the stimulus has been removed, the stimulation-drive begins to drift back to the
homeostatic regime (one of the many regulatory responses in this example).
Interaction Dynamics
The behavior system produces interaction dynamics that are similar to the five phases
of infant social interactions (initiation, mutual-orientation, greeting, play-dialogue, and
disengagement) discussed in chapter 3. These dynamic phases are not explicitly represented
in the behavior system, but emerge from the interaction of the synthetic nervous system
withtheenvironment.Producingbehaviorsthatconveyintentionalityexploitsthecaregiver’s
natural tendencies to treat the robot as a social creature, and thus to respond in characteristic