Page 165 - Designing Sociable Robots
P. 165
breazeal-79017 book March 18, 2002 14:7
146 Chapter 9
There are four distinct motor systems that carry out these functions for Kismet. The
vocalization system produces expressive babbles that allow the robot to engage humans in
proto-dialogue. The face motor system orchestrates the robot’s emotive facial expressions
and body posture, its facial displays that serve communicative social functions, those that
serve behavioral functions (such as “sleeping”), and lip synchronization with accompanying
facial animation. The oculo-motor system produces human-like eye movements and head
orientations that serve important sensing as well as social functions. Finally, the motor
skills system coordinates each of these specialized motor systems to produce coherent
multi-modal motor acts.
Levels of Interaction
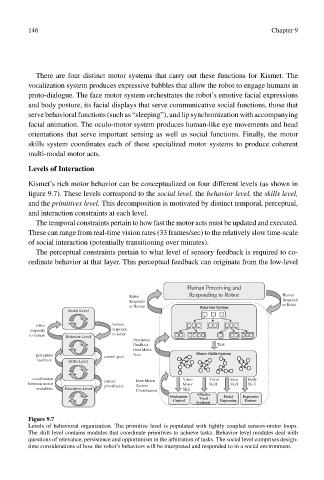
Kismet’s rich motor behavior can be conceptualized on four different levels (as shown in
figure 9.7). These levels correspond to the social level, the behavior level, the skills level,
and the primitives level. This decomposition is motivated by distinct temporal, perceptual,
and interaction constraints at each level.
The temporal constraints pertain to how fast the motor acts must be updated and executed.
These can range from real-time vision rates (33 frames/sec) to the relatively slow time-scale
of social interaction (potentially transitioning over minutes).
The perceptual constraints pertain to what level of sensory feedback is required to co-
ordinate behavior at that layer. This perceptual feedback can originate from the low-level
Human Perceiving and
Robot Responding to Robot Human
Responds
Responds
to Human Behavior System to Robot
Social Level
robot human
responds responds
to human Behavior Level to robot
Perceptual
Feedback Task
from Motor
perceptual current goal Acts Motor Skills System
feedback Skills Level
coordination Visuo- Vocal Face Body
current Inter-Motor
between motor primitive(s) System Motor Skill Skill Skill
modalities Primitives Level Skill
Coordination
Affective
Oculomotor Vocal Facial Expressive
Control Expression Posture
Synthesis
Figure 9.7
Levels of behavioral organization. The primitive level is populated with tightly coupled sensori-motor loops.
The skill level contains modules that coordinate primitives to achieve tasks. Behavior level modules deal with
questions of relevance, persistence and opportunism in the arbitration of tasks. The social level comprises design-
time considerations of how the robot’s behaviors will be interpreted and responded to in a social environment.