Page 282 - Distributed model predictive control for plant-wide systems
P. 282
256 Distributed Model Predictive Control for Plant-Wide Systems
Table 11.2 Computational burdens of DMPC and centralized MPC
Item Minimum time (s) Maximum time (s) Average time (s)
Constructing model of each subsystem 0.0008 0.0012 0.0009
DMPC with iteration l=1 0.0153 0.0484 0.0216
DMPC with iteration l=2 0.0268 0.0690 0.0452
DMPC with iteration l=3 0.0497 0.1194 0.0780
DMPC with iteration l=5 0.0895 0.3665 0.1205
Constructing model of overall system 0.0626 0.1871 0.0890
Centralized MPC 0.6535 1.8915 0.9831
Reference Cooling curve
Cooling curve
900
Temperature (°C) 800
700
600 0
0
2 10
4
6 20 Strip point
Time (s)
8
10 30
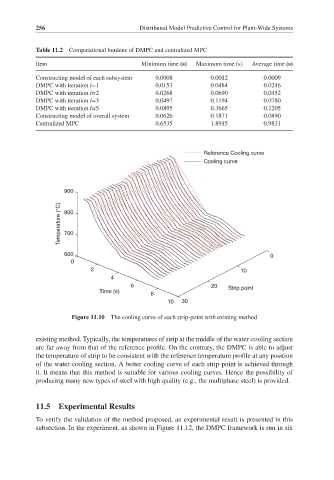
Figure 11.10 The cooling curve of each strip-point with existing method
existing method. Typically, the temperatures of strip at the middle of the water-cooling section
are far away from that of the reference profile. On the contrary, the DMPC is able to adjust
the temperature of strip to be consistent with the reference temperature profile at any position
of the water-cooling section. A better cooling curve of each strip-point is achieved through
it. It means that this method is suitable for various cooling curves. Hence the possibility of
producing many new types of steel with high quality (e.g., the multiphase steel) is provided.
11.5 Experimental Results
To verify the validation of the method proposed, an experimental result is presented in this
subsection. In the experiment, as shown in Figure 11.12, the DMPC framework is run in six