Page 279 - Distributed model predictive control for plant-wide systems
P. 279
Hot-Rolled Strip Laminar Cooling Process with Distributed Predictive Control 253
950
Model
900 Observer
850
2
x 3,2
800 x 2,2
2
Temperture (°C) 750 x 1,2
2
700
6
650 x 3,2
6
x 2,2 10 10 10
600 x 1,2 x 2,2 x 3,2
6
x 1,2 14 14
550 x 2,3 x 3,3
14
x 1,3
500
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
Time (s)
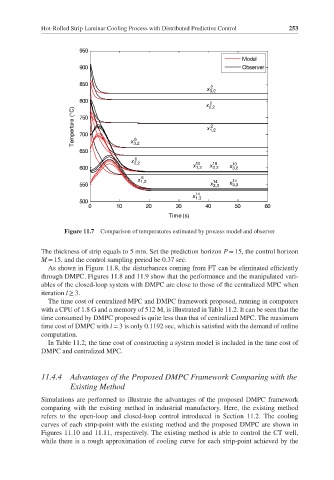
Figure 11.7 Comparison of temperatures estimated by process model and observer
The thickness of strip equals to 5 mm. Set the prediction horizon P = 15, the control horizon
M = 15, and the control sampling period be 0.37 sec.
As shown in Figure 11.8, the disturbances coming from FT can be eliminated efficiently
through DMPC. Figures 11.8 and 11.9 show that the performance and the manipulated vari-
ables of the closed-loop system with DMPC are close to those of the centralized MPC when
iteration l ≥ 3.
The time cost of centralized MPC and DMPC framework proposed, running in computers
with a CPU of 1.8 G and a memory of 512 M, is illustrated in Table 11.2. It can be seen that the
time consumed by DMPC proposed is quite less than that of centralized MPC. The maximum
time cost of DMPC with l = 3 is only 0.1192 sec, which is satisfied with the demand of online
computation.
In Table 11.2, the time cost of constructing a system model is included in the time cost of
DMPC and centralized MPC.
11.4.4 Advantages of the Proposed DMPC Framework Comparing with the
Existing Method
Simulations are performed to illustrate the advantages of the proposed DMPC framework
comparing with the existing method in industrial manufactory. Here, the existing method
refers to the open-loop and closed-loop control introduced in Section 11.2. The cooling
curves of each strip-point with the existing method and the proposed DMPC are shown in
Figures 11.10 and 11.11, respectively. The existing method is able to control the CT well,
while there is a rough approximation of cooling curve for each strip-point achieved by the