Page 183 - Dynamics and Control of Nuclear Reactors
P. 183
180 CHAPTER 13 Boiling water reactors
(A)
(B)
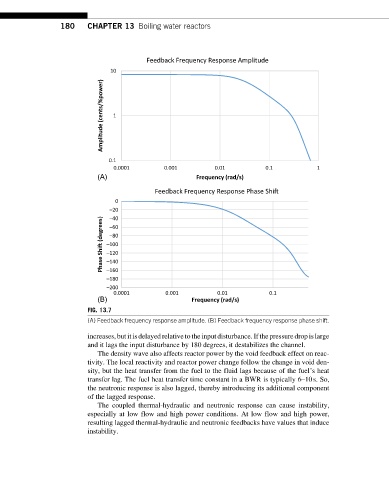
FIG. 13.7
(A) Feedback frequency response amplitude. (B) Feedback frequency response phase shift.
increases, but itis delayed relative to the input disturbance.If the pressure drop is large
and it lags the input disturbance by 180 degrees, it destabilizes the channel.
The density wave also affects reactor power by the void feedback effect on reac-
tivity. The local reactivity and reactor power change follow the change in void den-
sity, but the heat transfer from the fuel to the fluid lags because of the fuel’s heat
transfer lag. The fuel heat transfer time constant in a BWR is typically 6–10s. So,
the neutronic response is also lagged, thereby introducing its additional component
of the lagged response.
The coupled thermal-hydraulic and neutronic response can cause instability,
especially at low flow and high power conditions. At low flow and high power,
resulting lagged thermal-hydraulic and neutronic feedbacks have values that induce
instability.