Page 278 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 278
M04_CHAF9601_04_SE_C04.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:11 Page 245
Chapter 4 E-environment 245
which may ultimately be reduced to five companies that BT will enter into a formal
arrangement with each year.
4 Technology mining. A traditional literature review of technologies described in published
documents. Deutsche Telekom AG is given as an example. They use technology to auto-
mate the process through software such as Autonomy which searches for patterns indi-
cating potential technology solutions within patents, articles, journals, technological
reports and trend studies. A simpler approach is setting up a keyword search for tech-
nologies through a free service such as Google Alerts (www.google.com/alerts).
It may also be useful to identify how rapidly a new concept is being adopted. When a prod-
uct or service is adopted rapidly this is known as ‘rapid diffusion’. The access to the Internet
is an example of this. In developed countries the use of the Internet has become widespread
more rapidly than the use of TV, for example. It seems that in relation to Internet access and
interactive TV, Internet-enabled mobile phones are relatively slow-diffusion products!
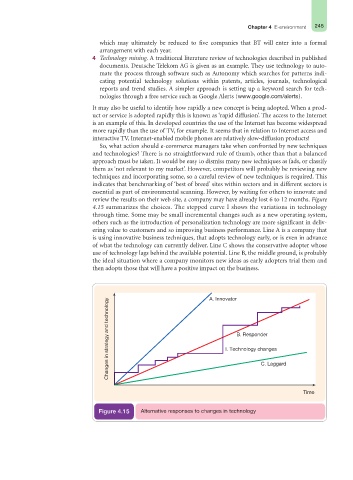
So, what action should e-commerce managers take when confronted by new techniques
and technologies? There is no straightforward rule of thumb, other than that a balanced
approach must be taken. It would be easy to dismiss many new techniques as fads, or classify
them as ‘not relevant to my market’. However, competitors will probably be reviewing new
techniques and incorporating some, so a careful review of new techniques is required. This
indicates that benchmarking of ‘best of breed’ sites within sectors and in different sectors is
essential as part of environmental scanning. However, by waiting for others to innovate and
review the results on their web site, a company may have already lost 6 to 12 months. Figure
4.15 summarizes the choices. The stepped curve I shows the variations in technology
through time. Some may be small incremental changes such as a new operating system,
others such as the introduction of personalization technology are more significant in deliv-
ering value to customers and so improving business performance. Line A is a company that
is using innovative business techniques, that adopts technology early, or is even in advance
of what the technology can currently deliver. Line C shows the conservative adopter whose
use of technology lags behind the available potential. Line B, the middle ground, is probably
the ideal situation where a company monitors new ideas as early adopters trial them and
then adopts those that will have a positive impact on the business.
technology A. Innovator
and B. Responder
strategy I. Technology changes
in
Changes C. Laggard
Time
Figure 4.15 Alternative responses to changes in technology