Page 145 - Educational Technology A Primer for the 21st Century
P. 145
136 8 Designing Learning Activities and Instructional Systems
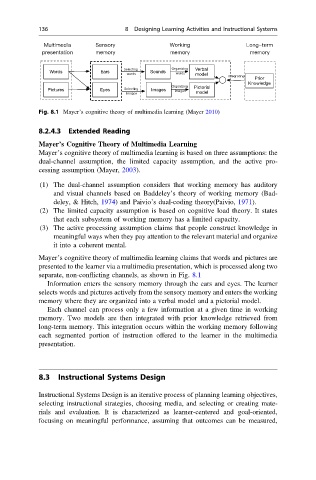
Fig. 8.1 Mayer’s cognitive theory of multimedia learning (Mayer 2010)
8.2.4.3 Extended Reading
Mayer’s Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning
Mayer’s cognitive theory of multimedia learning is based on three assumptions: the
dual-channel assumption, the limited capacity assumption, and the active pro-
cessing assumption (Mayer, 2003).
(1) The dual-channel assumption considers that working memory has auditory
and visual channels based on Baddeley’s theory of working memory (Bad-
deley, & Hitch, 1974) and Paivio’s dual-coding theory(Paivio, 1971).
(2) The limited capacity assumption is based on cognitive load theory. It states
that each subsystem of working memory has a limited capacity.
(3) The active processing assumption claims that people construct knowledge in
meaningful ways when they pay attention to the relevant material and organize
it into a coherent mental.
Mayer’s cognitive theory of multimedia learning claims that words and pictures are
presented to the learner via a multimedia presentation, which is processed along two
separate, non-conflicting channels, as shown in Fig. 8.1
Information enters the sensory memory through the ears and eyes. The learner
selects words and pictures actively from the sensory memory and enters the working
memory where they are organized into a verbal model and a pictorial model.
Each channel can process only a few information at a given time in working
memory. Two models are then integrated with prior knowledge retrieved from
long-term memory. This integration occurs within the working memory following
each segmented portion of instruction offered to the learner in the multimedia
presentation.
8.3 Instructional Systems Design
Instructional Systems Design is an iterative process of planning learning objectives,
selecting instructional strategies, choosing media, and selecting or creating mate-
rials and evaluation. It is characterized as learner-centered and goal-oriented,
focusing on meaningful performance, assuming that outcomes can be measured,