Page 204 - Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
P. 204
Chapter 7 Induction motors 199
balanced, three-phase, a.c. supply, then the conventional two-axis, or d-q, approach to
motor modelling can be used to analyse the operation of the induction motor. This
approach permits the time-varying motor parameters to be eliminated, and the motor
variables can be expressed relative to a set of mutually decoupled orthogonal axes, which
are commonly termed the direct and the quadrature axes.
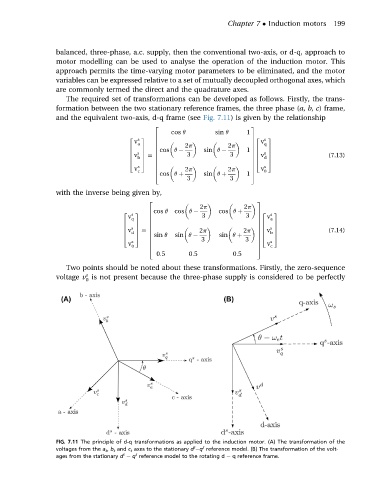
The required set of transformations can be developed as follows. Firstly, the trans-
formation between the two stationary reference frames, the three phase (a, b, c) frame,
and the equivalent two-axis, d-q frame (see Fig. 7.11) is given by the relationship
2 3
cos q sin q 1
2 s 3 6 7 v s 3
72
v a 6 q
6 2p 2p 7
cos q sin q
6 7 6 1 76 7
6 s 7 6 3 3 76 s 7 (7.13)
d
b
6 v 7 ¼ 6 76 v 7
4 5 6 74 5
v s 6 2p 2p 7 v s
6
7
c 0
4 1 5
cos q þ sin q þ
3 3
with the inverse being given by,
2 3
2p 2p
6 cos q cos q cos q þ
v q 6 a
2 s 3 3 3 7 v s 3
72
6 7
6 7 6 76 7
6 s 7 6 2p 76 s 7 (7.14)
b
d
6 v 7 ¼ 6 2p 76 v 7
6 sin q
4 5 sin q 3 sin q þ 3 74 5
v s 6 7 v s
6
7
0 c
4 5
0:5 0:5 0:5
Two points should be noted about these transformations. Firstly, the zero-sequence
s
voltage v is not present because the three-phase supply is considered to be perfectly
0
FIG. 7.11 The principle of d-q transformations as applied to the induction motor. (A) The transformation of the
s
s
voltages from the a s , b s and c s axes to the stationary d q reference model. (B) The transformation of the volt-
s
s
ages from the stationary d e q reference model to the rotating d e q reference frame.