Page 201 - Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
P. 201
196 Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
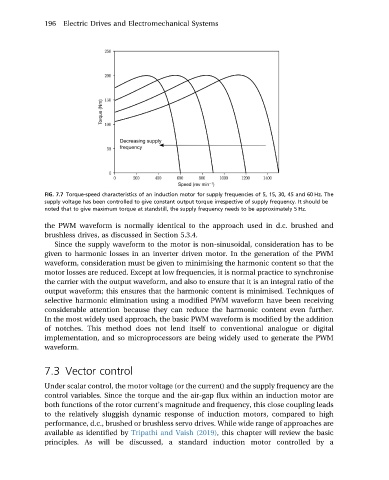
FIG. 7.7 Torque-speed characteristics of an induction motor for supply frequencies of 5, 15, 30, 45 and 60 Hz. The
supply voltage has been controlled to give constant output torque irrespective of supply frequency. It should be
noted that to give maximum torque at standstill, the supply frequency needs to be approximately 5 Hz.
the PWM waveform is normally identical to the approach used in d.c. brushed and
brushless drives, as discussed in Section 5.3.4.
Since the supply waveform to the motor is non-sinusoidal, consideration has to be
given to harmonic losses in an inverter driven motor. In the generation of the PWM
waveform, consideration must be given to minimising the harmonic content so that the
motor losses are reduced. Except at low frequencies, it is normal practice to synchronise
the carrier with the output waveform, and also to ensure that it is an integral ratio of the
output waveform; this ensures that the harmonic content is minimised. Techniques of
selective harmonic elimination using a modified PWM waveform have been receiving
considerable attention because they can reduce the harmonic content even further.
In the most widely used approach, the basic PWM waveform is modified by the addition
of notches. This method does not lend itself to conventional analogue or digital
implementation, and so microprocessors are being widely used to generate the PWM
waveform.
7.3 Vector control
Under scalar control, the motor voltage (or the current) and the supply frequency are the
control variables. Since the torque and the air-gap flux within an induction motor are
both functions of the rotor current’s magnitude and frequency, this close coupling leads
to the relatively sluggish dynamic response of induction motors, compared to high
performance, d.c., brushed or brushless servo drives. While wide range of approaches are
available as identified by Tripathi and Vaish (2019), this chapter will review the basic
principles. As will be discussed, a standard induction motor controlled by a