Page 233 - Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
P. 233
Chapter 9 Related motors and actuators 229
magnetic flux destiny, B, the current, i, hence for a winding of N turns, the resultant force
is given by,
F ¼ BLiN (9.1)
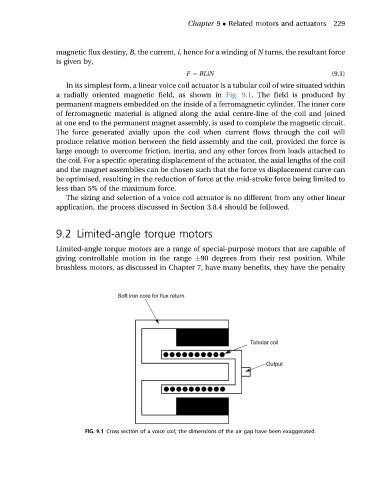
In its simplest form, a linear voice coil actuator is a tubular coil of wire situated within
a radially oriented magnetic field, as shown in Fig. 9.1. The field is produced by
permanent magnets embedded on the inside of a ferromagnetic cylinder. The inner core
of ferromagnetic material is aligned along the axial centre-line of the coil and joined
at one end to the permanent magnet assembly, is used to complete the magnetic circuit.
The force generated axially upon the coil when current flows through the coil will
produce relative motion between the field assembly and the coil, provided the force is
large enough to overcome friction, inertia, and any other forces from loads attached to
the coil. For a specific operating displacement of the actuator, the axial lengths of the coil
and the magnet assemblies can be chosen such that the force vs displacement curve can
be optimised, resulting in the reduction of force at the mid-stroke force being limited to
less than 5% of the maximum force.
The sizing and selection of a voice coil actuator is no different from any other linear
application, the process discussed in Section 3.8.4 should be followed.
9.2 Limited-angle torque motors
Limited-angle torque motors are a range of special-purpose motors that are capable of
giving controllable motion in the range 90 degrees from their rest position. While
brushless motors, as discussed in Chapter 7, have many benefits, they have the penalty
FIG. 9.1 Cross section of a voice coil; the dimensions of the air gap have been exaggerated.