Page 235 - Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
P. 235
Chapter 9 Related motors and actuators 231
In the selection of a limited-angle torque motor for an application, a number of
parameters shall be considered, including:
Peak torque. As in a conventional motor, this is the torque which is developed at
the rated current.
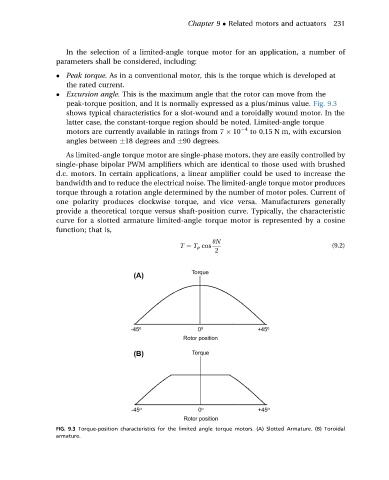
Excursion angle. This is the maximum angle that the rotor can move from the
peak-torque position, and it is normally expressed as a plus/minus value. Fig. 9.3
shows typical characteristics for a slot-wound and a toroidally wound motor. In the
latter case, the constant-torque region should be noted. Limited-angle torque
motors are currently available in ratings from 7 10 4 to 0.15 N m, with excursion
angles between 18 degrees and 90 degrees.
As limited-angle torque motor are single-phase motors, they are easily controlled by
single-phase bipolar PWM amplifiers which are identical to those used with brushed
d.c. motors. In certain applications, a linear amplifier could be used to increase the
bandwidth and to reduce the electrical noise. The limited-angle torque motor produces
torque through a rotation angle determined by the number of motor poles. Current of
one polarity produces clockwise torque, and vice versa. Manufacturers generally
provide a theoretical torque versus shaft-position curve. Typically, the characteristic
curve for a slotted armature limited-angle torque motor is represented by a cosine
function; that is,
qN
T ¼ T p cos (9.2)
2
FIG. 9.3 Torque-position characteristics for the limited angle torque motors. (A) Slotted Armature. (B) Toroidal
armature.