Page 238 - Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
P. 238
234 Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
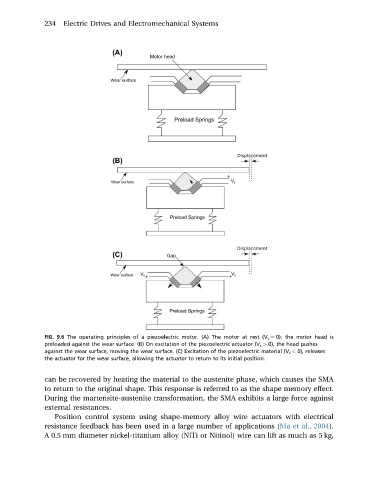
FIG. 9.6 The operating principles of a piezoelectric motor. (A) The motor at rest (V s ¼ 0): the motor head is
preloaded against the wear surface. (B) On excitation of the piezoelectric actuator (V s > 0), the head pushes
against the wear surface, moving the wear surface. (C) Excitation of the piezoelectric material (V s < 0), releases
the actuator for the wear surface, allowing the actuator to return to its initial position.
can be recovered by heating the material to the austenite phase, which causes the SMA
to return to the original shape. This response is referred to as the shape memory effect.
During the martensite-austenite transformation, the SMA exhibits a large force against
external resistances.
Position control system using shape-memory alloy wire actuators with electrical
resistance feedback has been used in a large number of applications (Ma et al., 2004).
A 0.5 mm diameter nickel-titanium alloy (NiTi or Nitinol) wire can lift as much as 5 kg,