Page 281 - Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
P. 281
278 Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
data exchange for applications. The relationship between the OSI and TCP/IP models are
shown in Fig. 11.3.
11.1.4 Industrial specific networking
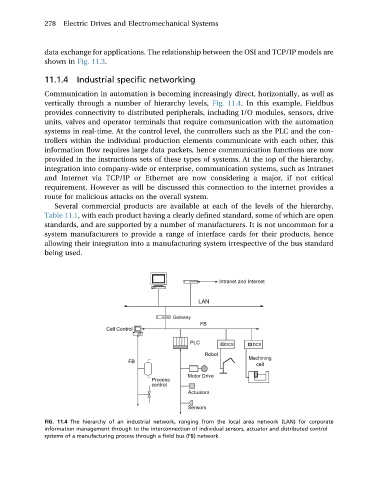
Communication in automation is becoming increasingly direct, horizontally, as well as
vertically through a number of hierarchy levels, Fig. 11.4. In this example, Fieldbus
provides connectivity to distributed peripherals, including I/O modules, sensors, drive
units, valves and operator terminals that require communication with the automation
systems in real-time. At the control level, the controllers such as the PLC and the con-
trollers within the individual production elements communicate with each other, this
information flow requires large data packets, hence communication functions are now
provided in the instructions sets of these types of systems. At the top of the hierarchy,
integration into company-wide or enterprise, communication systems, such as Intranet
and Internet via TCP/IP or Ethernet are now considering a major, if not critical
requirement. However as will be discussed this connection to the internet provides a
route for malicious attacks on the overall system.
Several commercial products are available at each of the levels of the hierarchy,
Table 11.1, with each product having a clearly defined standard, some of which are open
standards, and are supported by a number of manufacturers. It is not uncommon for a
system manufacturers to provide a range of interface cards for their products, hence
allowing their integration into a manufacturing system irrespective of the bus standard
being used.
FIG. 11.4 The hierarchy of an industrial network, ranging from the local area network (LAN) for corporate
information management through to the interconnection of individual sensors, actuator and distributed control
systems of a manufacturing process through a field bus (FB) network.