Page 285 - Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
P. 285
282 Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
11.3.1 Internet of things
The Internet of Things (IoTs) is a computing concept that describes an approach where a
wide range of objects are connected directly to the Internet. This allows the deployment
of smart sensors capable of sensing the surrounding environment, transmitting and
processing acquired data, and then using smart actuators to interact with the environ-
ment. This has resulted in a wide range of consumer-based applications including home
automation, energy management and health monitoring.
The Industrial IoT (IIoT) is a sub-set of IoT that describes machine-to-machine
(m2m) and industrial communication technologies as applied to manufacturing and
process applications. While both approaches are similar the Industrial IoT has a number
of key differences, in particular each application has low risk, a degree of resilience is
incorporated, and the overall network of application tends to be larger than an IoT
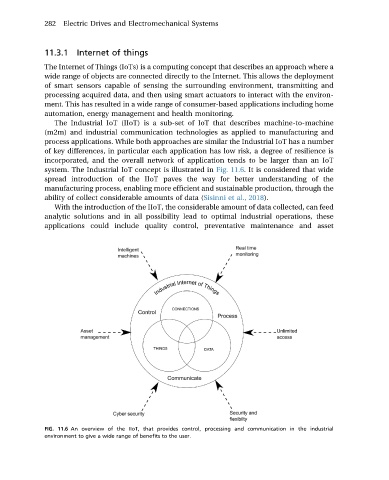
system. The Industrial IoT concept is illustrated in Fig. 11.6. It is considered that wide
spread introduction of the IIoT paves the way for better understanding of the
manufacturing process, enabling more efficient and sustainable production, through the
ability of collect considerable amounts of data (Sisinni et al., 2018).
With the introduction of the IIoT, the considerable amount of data collected, can feed
analytic solutions and in all possibility lead to optimal industrial operations, these
applications could include quality control, preventative maintenance and asset
FIG. 11.6 An overview of the IIoT, that provides control, processing and communication in the industrial
environment to give a wide range of benefits to the user.