Page 166 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 166
128 Electromechanical Devices & Components Illustrated Sourcebook
Uses for electrical heating are nearly as numerous as motor
applications. We find electrical heating elements wherever we
go. Our kitchens have toasters, stove tops, crock pots, coffee
makers, and various other appliances, all with electrical heat-
Schematic Symbol
ing elements. Our hair dryers and curlers have electrical heat-
ing elements. Many of our hot water heaters and home heating
systems rely on electrical heating. Just by looking around as Protective Lip
you go through your day-to-day life, you’ll see hundreds of
electrical heating applications.
Most heating elements are resistive in nature. That is to say
Coiled Ni-Chrome Element
that the heating element represents a high-power resistor.
When a current is passed through the element, it glows red hot
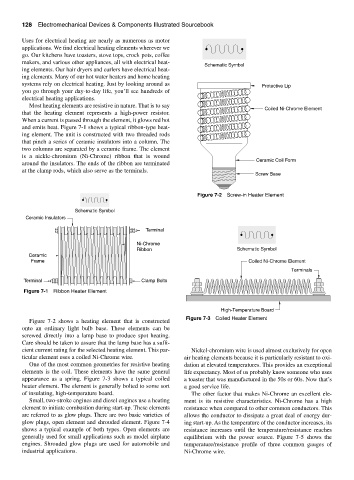
and emits heat. Figure 7-1 shows a typical ribbon-type heat-
ing element. The unit is constructed with two threaded rods
that pinch a series of ceramic insulators into a column. The
two columns are separated by a ceramic frame. The element
is a nickle-chromium (Ni-Chrome) ribbon that is wound
Ceramic Coil Form
around the insulators. The ends of the ribbon are terminated
at the clamp rods, which also serve as the terminals.
Screw Base
Figure 7-2 Screw-in Heater Element
Schematic Symbol
Ceramic Insulators
Terminal
Ni-Chrome
Ribbon Schematic Symbol
Ceramic
Frame Coiled Ni-Chrome Element
Terminals
Terminal Clamp Bolts
Figure 7-1 Ribbon Heater Element
High-Temperature Board
Figure 7-3 Coiled Heater Element
Figure 7-2 shows a heating element that is constructed
onto an ordinary light bulb base. These elements can be
screwed directly into a lamp base to produce spot heating.
Care should be taken to assure that the lamp base has a suffi-
cient current rating for the selected heating element. This par- Nickel-chromium wire is used almost exclusively for open
ticular element uses a coiled Ni-Chrome wire. air heating elements because it is particularly resistant to oxi-
One of the most common geometries for resistive heating dation at elevated temperatures. This provides an exceptional
elements is the coil. These elements have the same general life expectancy. Most of us probably know someone who uses
appearance as a spring. Figure 7-3 shows a typical coiled a toaster that was manufactured in the 50s or 60s. Now that’s
heater element. The element is generally bolted to some sort a good service life.
of insulating, high-temperature board. The other factor that makes Ni-Chrome an excellent ele-
Small, two-stroke engines and diesel engines use a heating ment is its resistive characteristics. Ni-Chrome has a high
element to initiate combustion during start-up. These elements resistance when compared to other common conductors. This
are referred to as glow plugs. There are two basic varieties of allows the conductor to dissipate a great deal of energy dur-
glow plugs, open element and shrouded element. Figure 7-4 ing start-up. As the temperature of the conductor increases, its
shows a typical example of both types. Open elements are resistance increases until the temperature/resistance reaches
generally used for small applications such as model airplane equilibrium with the power source. Figure 7-5 shows the
engines. Shrouded glow plugs are used for automobile and temperature/resistance profile of three common gauges of
industrial applications. Ni-Chrome wire.