Page 240 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 240
202 Electromechanical Devices & Components Illustrated Sourcebook
Front of Microphone Parabolic Reflector
Microphone Post Microphone
Omnidirectional Cardioid Hypercardioid Bidirectional Shotgun Microphone Cable Sound
Signal
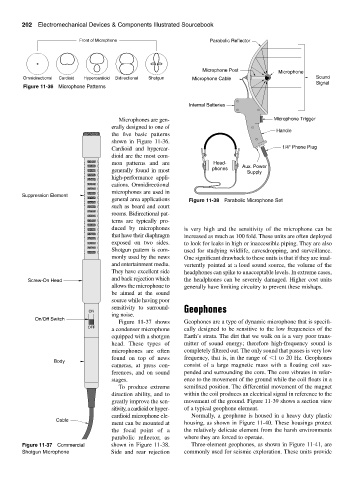
Figure 11-36 Microphone Patterns
Internal Batteries
Microphones are gen- Microphone Trigger
erally designed to one of
Handle
the five basic patterns
shown in Figure 11-36.
Cardioid and hypercar- 1/4" Phone Plug
dioid are the most com-
mon patterns and are Head- Aux. Power
generally found in most phones Supply
high-performance appli-
cations. Omnidirectional
microphones are used in
Suppression Element
general area applications Figure 11-38 Parabolic Microphone Set
such as board and court
rooms. Bidirectional pat-
terns are typically pro-
duced by microphones is very high and the sensitivity of the microphone can be
that have their diaphragm increased as much as 100 fold. These units are often deployed
exposed on two sides. to look for leaks in high or inaccessible piping. They are also
Shotgun pattern is com- used for studying wildlife, eavesdropping, and surveillance.
monly used by the news One significant drawback to these units is that if they are inad-
and entertainment media. vertently pointed at a loud sound source, the volume of the
They have excellent side headphones can spike to unacceptable levels. In extreme cases,
and back rejection which
Screw-On Head the headphones can be severely damaged. Higher cost units
allows the microphone to generally have limiting circuitry to prevent these mishaps.
be aimed at the sound
source while having poor
sensitivity to surround- Geophones
ON
ing noise.
On/Off Switch
Figure 11-37 shows Geophones are a type of dynamic microphone that is specifi-
OFF
a condenser microphone cally designed to be sensitive to the low frequencies of the
equipped with a shotgun Earth’s strata. The dirt that we walk on is a very poor trans-
head. These types of mitter of sound energy; therefore high-frequency sound is
microphones are often completely filtered out. The only sound that passes is very low
found on top of news frequency, that is, in the range of
1 to 20 Hz. Geophones
Body
cameras, at press con- consist of a large magnetic mass with a floating coil sus-
ferences, and on sound pended and surrounding the core. The core vibrates in refer-
stages. ence to the movement of the ground while the coil floats in a
To produce extreme semifixed position. The differential movement of the magnet
direction ability, and to within the coil produces an electrical signal in reference to the
greatly improve the sen- movement of the ground. Figure 11-39 shows a section view
sitivity,a cardioid or hyper- of a typical geophone element.
cardioid microphone ele- Normally, a geophone is housed in a heavy duty plastic
Cable
ment can be mounted at housing, as shown in Figure 11-40. These housings protect
the focal point of a the relatively delicate element from the harsh environments
parabolic reflector, as where they are forced to operate.
Figure 11-37 Commercial shown in Figure 11-38. Three-element geophones, as shown in Figure 11-41, are
Shotgun Microphone Side and rear rejection commonly used for seismic exploration. These units provide