Page 239 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 239
Chapter 11 Acoustic Devices 201
Mouthpiece
Coaxial Cable
Schematic
Symbol
Shielded Housing
Plastic Housing
Bend Relief
Felt Cap
1/8" Phone Plug
Cable
Power (V+)
Figure 11-33 Condenser Microphone Cartridge
Figure 11-31 Piezo Crystal Microphone
Wind Shield
Crystal microphones are most commonly found in inex- Screw On Head
pensive units, as shown in Figure 11-31, or as musical instru-
On/Off Switch Body
ment pickups. These units are very inexpensive and generally
produce a good quality output.
Condenser microphones operate on a variable capacitance ON OFF
principle. Figure 11-32 shows a schematic representation of a
basic condenser microphone. A diaphragm is vibrated in ref-
Cable
erence to a fixed electrode. A small local battery provides
power to the circuit. As the diaphragm vibrates, the capaci- Figure 11-34 Commercial Condenser Microphone
tance of the circuit changes in reference to the sound. The
output of the element is processed through a preamplifier and
into the audio equipment.
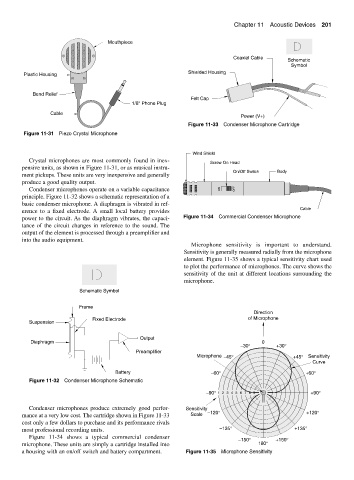
Microphone sensitivity is important to understand.
Sensitivity is generally measured radially from the microphone
element. Figure 11-35 shows a typical sensitivity chart used
to plot the performance of microphones. The curve shows the
sensitivity of the unit at different locations surrounding the
microphone.
Schematic Symbol
Frame
Direction
Fixed Electrode of Microphone
Suspension
Output
Diaphragm 0
−30° +30°
Preamplifier
Microphone −45° +45° Sensitivity
Curve
Battery −60° +60°
Figure 11-32 Condenser Microphone Schematic
−90° 12 3 4 5 6789 +90°
Condenser microphones produce extremely good perfor- Sensitivity
mance at a very low cost. The cartridge shown in Figure 11-33 Scale −120° +120°
cost only a few dollars to purchase and its performance rivals
most professional recording units. −135° +135°
Figure 11-34 shows a typical commercial condenser −150° +150°
microphone. These units are simply a cartridge installed into 180°
a housing with an on/off switch and battery compartment. Figure 11-35 Microphone Sensitivity