Page 269 - Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 3rd Edition
P. 269
Sec. 5.2 Method of Initial Rates 241
T,aking the log of both sides of Equation (E5-3.1), we have
ln[- '*lo = Ink + 01 In C,,,,, (135-3.2)
The derivative at time t = 0 can be found from the slope of the plot of concentra-
tion versus time evaluated at t = 0. Figure E5-3.l(a) and (b) give
4 N HC1 solution 1 N HC1 solution
-
3.9982 - 4.0000 0.9987 - 1.0000
-rHclo = - 5- 0 -~HCI,O = - 6- 0
-~Hc~,o 3.6 X g mol/dm3 - min - r,,,,, = 2.2 X 10-4g moVdm3. min
Converting to a rate per unit area, - r: , and to seconds (30 cm2 of solid per liter of
solution), the rates at 1 N and 4 N become 1.2 X mol/cm2.s and
2.0 X rnol/cm2. s, respectively. We also could have used either POLYMATH
01 the differentiation formulas to find the derivative at t = 0.
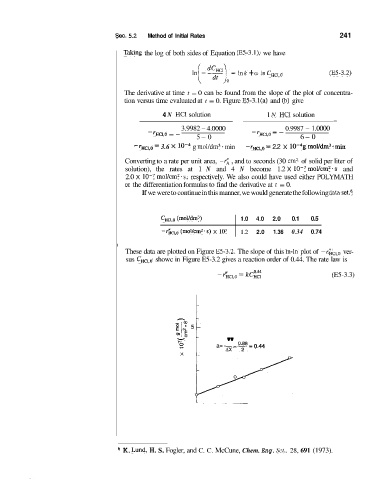
If we were to continue in this manner, we would generate the following da,ta set.6
c,cl,o (moYdm3! 1.0 4.0 2.0 0.1 0.5
-rhc,,o (moVcm2.s) lo7 1.2 2.0 1.36 0.34 0.74
X
I
These data are plotted on Figure E5-3.2. The slope of this In-ln plot of ver-
sus C,,,,, showc in Figure E5-3.2 gives a reaction order of 0.44. The rate law is
(E5-3.3)
-
I
n-
v
c
9 a=-- '' Q'88- 0.44
AXx-'2 -
x -
K. Imd, H. S. Fogler, and C. C. McCune, Chem. Eng. Sci., 28, 691 (1973).