Page 46 - Embedded Microprocessor Systems Real World Design
P. 46
Multichip Designs
While the similarity between singlechip and multichip designs shown in Figure 2.1
is correct, it is somewhat misleading. The architectures are similar, but in the real
world, a multichip design usually is more complex. There usually is more memory
and generally more (or more complicated) 1/0 ports. A singlechip micro-
controller may not be suitable for a design for many reasons: insufficient 1/0 pins,
insufficient RAM or ROM, or any of the other considerations detailed in Chapter
1. However, once a decision has been made to go to a multichip implementation,
you take a quantum step in complexity.
A multichip design usually has most or all of the following as separate
components:
Microprocessor
Random access memory (RAM)
Programmable read-only memory (PROM)
Peripherals (I/O devices)
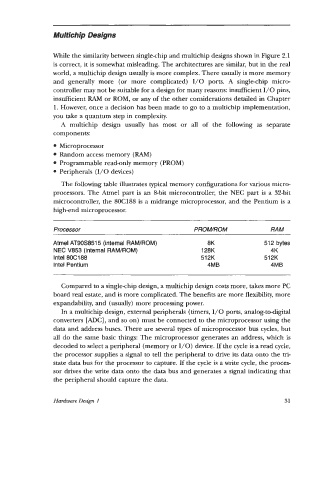
The following table illustrates typical memory configurations for various micro-
processors. The Atmel part is an &bit microcontroller, the NEC part is a 32-bit
microcontroller, the 8OC188 is a midrange microprocessor, and the Pentium is a
high-end microprocessor.
Processor PROM/ROM RAM
Atmel AT9OS8515 (internal RAM/ROM) 8K 51 2 bytes
NEC V853 (internal RAM/ROM) 128K 4K
Intel 80C188 512K 51 2K
Intel Pentium 4MB 4MB
Compared to a single-chip design, a multichip design costs more, takes more PC
board real estate, and is more complicated. The benefits are more flexibility, more
expandability, and (usually) more processing power.
In a multichip design, external peripherals (timers, 1/0 ports, analog-tu-digital
converters [ADC] , and so on) must be connected to the microprocessor using the
data and address buses. There are several types of microprocessor bus cycles, but
all do the same basic things: The microprocessor generates an address, which is
decoded to select a peripheral (memory or I/O) device. If the cycle is a read cycle,
the processor supplies a signal to tell the peripheral to drive its data onto the tri-
state data bus for the processor to capture. If the cycle is a write cycle, the proces-
sor drives the write data onto the data bus and generates a signal indicating that
the peripheral should capture the data.
Hardware Design 1 31