Page 50 - Embedded Microprocessor Systems Real World Design
P. 50
DATA Bus
TO PERIPHERALS
AND MEMORY
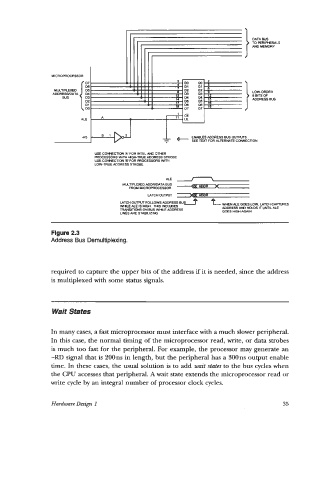
MICROPROCESSOR
LOW-ORDER
B BITS OF
ADDRESS BUS
USE CONNECTION 'A FOR INTEL AND OTHER
PROCESSORS WITH HlOKTRUE ADDRESS STROeE
FOR
USE CONNECT ON 'I PROCESSORS WITH
LOW-TRUE ADDRESS STROBE
Figure 2.3
Address Bus Demultiplexing.
required to capture the upper bits of the address if it is needed, since the address
is multiplexed with some status signals.
Wait States
In many cases, a fast microprocessor must interface with a much slower peripheral.
In this case, the normal timing of the microprocessor read, write, or data strobes
is much too fast for the peripheral. For example, the processor may generate an
-RD signal that is 20011s in length, but the peripheral has a 30011s output enable
time. In these cases, the usual solution is to add wait stales to the bus cycles when
the CPU accesses that peripheral. A wait state extends the microprocessor read or
write cycle by an integral number of processor clock cycles.
Hardware Design 1 35