Page 52 - Embedded Microprocessor Systems Real World Design
P. 52
PERIPHERAL MUS1
REQUEST A WAIT
STATE HERE ... FORTHEPROCESSORTO
1 1 RECOGNIZE IT HERE.
I \ I I \ I \ I
CLOCK
\
ALE
WAIT REQUEST
FROM PERIPHERAL I
SRDY TO I86 I
-RD OR -WR
f
IF A WAIT STATE WERE NOT USED, dD WOULD
TERMINATE HERE, AS INDICATED BY THE
DASHED LINE. THE WAIT STATE EXTENDS -RD
BYONECLOCKCYCLE
WAIT REQUEST
FROM PERIPHERAL SRDY TO 186
186 CLOCK
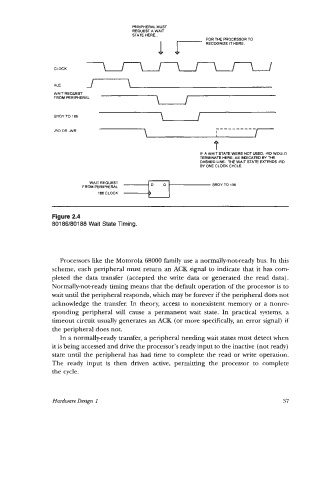
Figure 2.4
801 86/80188 Wait State Timing.
Processors like the Motorola 68000 family use a normally-not-ready bus. In this
scheme, each peripheral must return an ACK signal to indicate that it has com-
pleted the data transfer (accepted the write data or generated the read data).
Normally-not-ready timing means that the default operation of the processor is to
wait until the peripheral responds, which may be forever if the peripheral does not
acknowledge the transfer. In theory, access to nonexistent memory or a nonre-
sponding peripheral will cause a permanent wait state. In practical systems, a
timeout circuit usually generates an ACK (or more specifically, an error signal) if
the peripheral does not.
In a normally-ready transfer, a peripheral needing wait states must detect when
it is being accessed and drive the processor’s ready input to the inactive (not ready)
state until the peripheral has had time to complete the read or write operation.
The ready input is then driven active, permitting the processor to complete
the cycle.
Hardware Design I 37