Page 91 - Embedded Microprocessor Systems Real World Design
P. 91
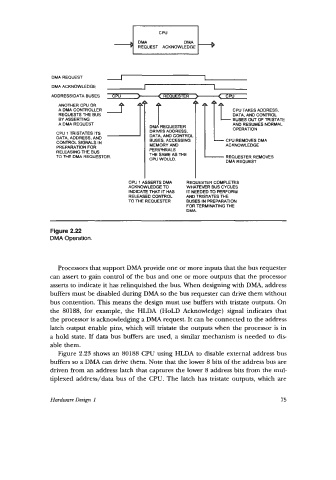
DMA REQUEST
DMA ACKNOWLEDGE
ADDRESSIDATA BUSES cw )-----(REQUESTER >-< C W
A DMA CONTROLLER f.
ANOTHER CPU OR
REQUESTS THE BUS CPU TAKES ADDRESS.
DATA, AND CONTROL
BY ASSERTING BUSES OUT OF TRISTATE
A DMA REQUEST AND RESUMES NORMAL
OPERATION
CPU 1 TRISTATES ITS
DATA, ADDRESS, AND BUSES, ACCESSING LL CPU REMOVES DMA
CONTROL SIGNALS IN
PREPARATION FOR ACKNOWLEDGE
RELEASING THE BUS
TO THE DMA REQUESTOR. THE SAME AS THE - REQUESTER REMOVES
CW WOULD. DMA REQUEST
CW 1 ASSERTS DMA REQUESTER COMPLETES
ACKNOWLEDGE TO WHATEVER BUS CYCLES
INDICATE THAT IT HAS IT NEEDED TO PERFORM
RELEASED CONTROL AND TRISTATES THE
TO THE REQUESTER BUSES IN PREPARATION
FOR TERMINATING THE
DMA.
Figure 2.22
DMA Operation.
Processors that support DMA provide one or more inputs that the bus requester
can assert to gain control of the bus and one or more outputs that the processor
asserts to indicate it has relinquished the bus. When designing with DMA, address
buffers must be disabled during DMA so the bus requester can drive them without
bus contention. This means the design must use buffers with tristate outputs. On
the 80188, for example, the HLDA (HOLD Acknowledge) signal indicates that
the processor is acknowledging a DMA request. It can be connected to the address
latch output enable pins, which will tristate the outputs when the processor is in
a hold state. If data bus buffers are used, a similar mechanism is needed to dis-
able them.
Figure 2.23 shows an 80188 CPU using HLDA to disable external address bus
buffers so a DMA can drive them. Note that the lower 8 bits of the address bus are
driven from an address latch that captures the lower 8 address bits from the mul-
tiplexed address/data bus of the CPU. The latch has tristate outputs, which are
Hardware Design I 75