Page 188 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 188
P1: FMX Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009J-69 July 19, 2001 22:50
688 Microanalytical Assays
both types of information. Usually in order to have repro-
ducible behavior, one of the electrodes is made smaller
than the other one, forcing the smaller electrode (working
electrode) to determine the current voltage behavior.
An important difference in the operating characteristics
of the two modes of operating electrochemical electrodes
is that in the amperometric mode, the limiting current is
directly proportional to the concentration of diffusion lim-
ited analyte. On the other hand, if the electrode is operated
in the potentiometric region the output is related to the ra-
tio of concentrations of oxidized and reduced forms of the
analyte. Thus operating in potentiometric mode results in
a system with a dynamic range of several orders of mag-
nitude (on the order of several hundredfold in concentra-
tion), while the amperometric mode of operation usually
has a dynamic range of tenfold.
Often in these devices one wants to be sure of the
potential at the working electrode, and in these cases a
three-electrode system is used that includes a reference
electrode. By using a reference electrode, one is more
certain of the electrical chemical events that are taking
place at the working electrode. When an electrode is op-
erated in an amperometric mode, the plateau regimes are
known as film limiting current regions. This current de-
pends on the rate of delivery of the electroactive species to
the working electrode, which in the case of bare electrodes
depends on the “stirring” in the vicinity of the electrode.
One of the primary breakthroughs that set off the explo-
sion in biosensors was Leland Clark’s invention of placing
a diffusion resistance film, in the form of a gas-permeable
membrane, in front of the working electrode. This film had
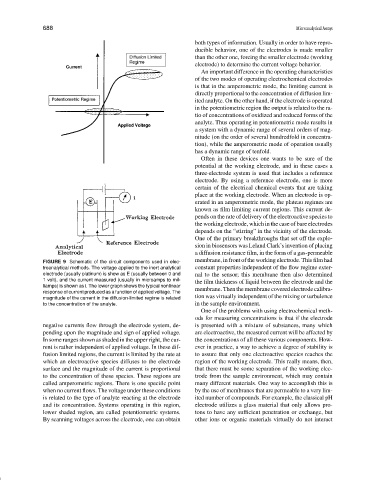
FIGURE 9 Schematic of the circuit components used in elec-
troanalytical methods. The voltage applied to the inert analytical constant properties independent of the flow regime exter-
electrode (usually platinum) is show as E (usually between 0 and nal to the sensor; this membrane then also determined
1 volt), and the current measured (usually in microamps to mil-
the film thickness of liquid between the electrode and the
liamps) is shown as i. The lower graph shows the typical nonlinear
response of current produced as a function of applied voltage. The membrane. Then the membrane covered electrode calibra-
magnitude of the current in the diffusion-limited regime is related tion was virtually independent of the mixing or turbulence
to the concentration of the analyte. in the sample environment.
One of the problems with using electrochemical meth-
ods for measuring concentrations is that if the electrode
negative currents flow through the electrode system, de- is presented with a mixture of substances, many which
pending upon the magnitude and sign of applied voltage. are electroactive, the measured current will be affected by
In some ranges shown as shaded in the upper right, the cur- the concentrations of all these various components. How-
rent is rather independent of applied voltage. In these dif- ever in practice, a way to achieve a degree of stability is
fusion limited regions, the current is limited by the rate at to assure that only one electroactive species reaches the
which an electroactive species diffuses to the electrode region of the working electrode. This really means, then,
surface and the magnitude of the current is proportional that there must be some separation of the working elec-
to the concentration of these species. These regions are trode from the sample environment, which may contain
called amperometric regions. There is one specific point many different materials. One way to accomplish this is
when no current flows. The voltage under these conditions by the use of membranes that are permeable to a very lim-
is related to the type of analyte reacting at the electrode ited number of compounds. For example, the classical pH
and its concentration. Systems operating in this region, electrode utilizes a glass material that only allows pro-
lower shaded region, are called potentiometric systems. tons to have any sufficient penetration or exchange, but
By scanning voltages across the electrode, one can obtain other ions or organic materials virtually do not interact