Page 181 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 181
P1: GGY Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN004D-156 June 8, 2001 15:28
24 Cryogenic Process Engineering
natural gas. Fortunately, since the major constituents of
natural gas have boiling points considerably higher than
that of helium, the separation can be accomplished with
condenser–evaporators rather than with the more expen-
sive rectification columns.
A typical scheme for separating helium from natural
gas was pioneered by the U.S. Bureau of Mines. In this
scheme, the natural gas is compressed to 4.13 MPa and
treated to remove water vapor, carbon dioxide, and hydro-
gensulfide.Thepurifiedstreamisthenpartiallycondensed
by the returning low-pressure, cold natural gas stream,
throttled to a pressure of 1.72 MPa, and further cooled
with cold nitrogen vapor in a heat exchanger–separator.
where 98% of the gas is liquefied. The cold nitrogen va-
por, supplied by an auxiliary refrigeration system, not only
provides the necessary cooling but also causes some recti-
fication of the gas phase in the heat exchanger, thereby in-
creasing the helium content. The remaining vapor phase,
consisting of about 60% helium and 40% nitrogen with
a very small amount of methane, is warmed to ambient
temperatures and sent to temporary storage pending fur-
ther purification. The liquid phase, having been depleted
of helium, is used to furnish the refrigeration required to
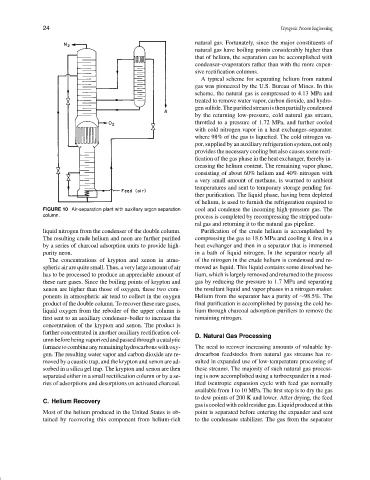
FIGURE 10 Air-separation plant with auxiliary argon separation cool and condense the incoming high-pressure gas. The
column. process is completed by recompressing the stripped natu-
ral gas and returning it to the natural gas pipeline.
liquid nitrogen from the condenser of the double column. Purification of the crude helium is accomplished by
The resulting crude helium and neon are further purified compressing the gas to 18.6 MPa and cooling it first in a
by a series of charcoal adsorption units to provide high- heat exchanger and then in a separator that is immersed
purity neon. in a bath of liquid nitrogen. In the separator nearly all
The concentrations of krypton and xenon in atmo- of the nitrogen in the crude helium is condensed and re-
spheric air are quite small. Thus, a very large amount of air moved as liquid. This liquid contains some dissolved he-
has to be processed to produce an appreciable amount of lium, which is largely removed and returned to the process
these rare gases. Since the boiling points of krypton and gas by reducing the pressure to 1.7 MPa and separating
xenon are higher than those of oxygen, these two com- the resultant liquid and vapor phases in a nitrogen maker.
ponents in atmospheric air tend to collect in the oxygen Helium from the separator has a purity of ∼98.5%. The
product of the double column. To recover these rare gases, final purification is accomplished by passing the cold he-
liquid oxygen from the reboiler of the upper column is lium through charcoal adsorption purifiers to remove the
first sent to an auxiliary condenser–boiler to increase the remaining nitrogen.
concentration of the krypton and xenon. The product is
further concentrated in another auxiliary rectification col- D. Natural Gas Processing
umn before being vaporized and passed through a catalytic
furnacetocombineanyremaininghydrocarbonswithoxy- The need to recover increasing amounts of valuable hy-
gen. The resulting water vapor and carbon dioxide are re- drocarbon feedstocks from natural gas streams has re-
moved by a caustic trap, and the krypton and xenon are ad- sulted in expanded use of low-temperature processing of
sorbed in a silica gel trap. The krypton and xenon are then these streams. The majority of such natural gas process-
separated either in a small rectification column or by a se- ing is now accomplished using a turboexpander in a mod-
ries of adsorptions and desorptions on activated charcoal. ified isentropic expansion cycle with feed gas normally
available from 1 to 10 MPa. The first step is to dry the gas
to dew points of 200 K and lower. After drying, the feed
C. Helium Recovery
gas is cooled with cold residue gas. Liquid produced at this
Most of the helium produced in the United States is ob- point is separated before entering the expander and sent
tained by recovering this component from helium-rich to the condensate stabilizer. The gas from the separator