Page 227 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 227
P1: GJC Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN004E-182 June 8, 2001 18:16
Distillation 551
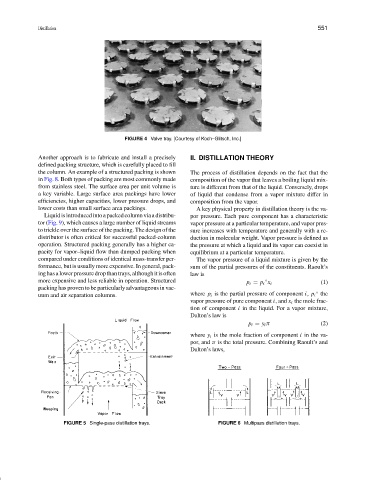
FIGURE 4 Valve tray. [Courtesy of Koch–Glitsch, Inc.]
Another approach is to fabricate and install a precisely II. DISTILLATION THEORY
defined packing structure, which is carefully placed to fill
the column. An example of a structured packing is shown The process of distillation depends on the fact that the
in Fig. 8. Both types of packing are most commonly made composition of the vapor that leaves a boiling liquid mix-
from stainless steel. The surface area per unit volume is ture is different from that of the liquid. Conversely, drops
a key variable. Large surface area packings have lower of liquid that condense from a vapor mixture differ in
efficiencies, higher capacities, lower pressure drops, and composition from the vapor.
lower costs than small surface area packings. A key physical property in distillation theory is the va-
Liquidisintroducedintoapackedcolumnviaadistribu- por pressure. Each pure component has a characteristic
tor (Fig. 9), which causes a large number of liquid streams vapor pressure at a particular temperature, and vapor pres-
to trickle over the surface of the packing. The design of the sure increases with temperature and generally with a re-
distributor is often critical for successful packed-column duction in molecular weight. Vapor pressure is defined as
operation. Structured packing generally has a higher ca- the pressure at which a liquid and its vapor can coexist in
pacity for vapor–liquid flow than dumped packing when equilibrium at a particular temperature.
compared under conditions of identical mass-transfer per- The vapor pressure of a liquid mixture is given by the
formance, but is usually more expensive. In general, pack- sum of the partial pressures of the constituents. Raoult’s
inghasalowerpressuredropthantrays,althoughitisoften law is
more expensive and less reliable in operation. Structured ◦
p i = p i x i (1)
packing has proven to be particularly advantageous in vac-
◦
uum and air separation columns. where p i is the partial pressure of component i, p i the
vapor pressure of pure component i, and x i the mole frac-
tion of component i in the liquid. For a vapor mixture,
Dalton’slawis
p i = y i π (2)
where y i is the mole fraction of component i in the va-
por, and π is the total pressure. Combining Raoult’s and
Dalton’s laws,
FIGURE 5 Single-pass distillation trays. FIGURE 6 Multipass distillation trays.