Page 292 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 292
P1: FYK/LPB P2: FPP Final
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN006C-252 June 27, 2001 14:15
92 Fluid Mixing
the fine particle sizes, the average particle sizes, and the
coarse particle sizes, since the leaching curves are often
quite different. In addition, the suspension of the fine, av-
erage, and coarse particles may be different in the leach
tank due to the fact that all these particles may not be
completely uniform throughout the system.
Typical design of an industrial leaching system looks
at the extraction rate versus time and power level and de-
termines the optimum combination of tank size and mixer
horsepower in terms of return on the product leached.
B. Industrial Examples
FIGURE 18 Typical comparison of power required for axial flow
One area for industrial studies is the whole area of slurry
impeller compared to radial flow impellers in solids suspension.
pipelines. Coal is by far the most common material in
settled solids), power becomes extremely high and ap- slurry pipelines, but other pipelines, but other pipelines
proaches infinity where there is no supernatant liquid left include iron ore and potash. In large volume solid suspen-
in the tank. To evaluate this effect, a mixing viscosimeter is sion applications, there is a considerable trade-off between
valuable, in which the slurry is agitated at the same time volume of a tank, mixer horsepower, shape of a tank, and
that the viscosity is measured, so that the measurement many other areas of cost consideration that are important
gives a reasonable value for the overall slurry. in overall design. In addition to the tanks in these sorts of
slurry systems, it must be capable of incorporating slurries
A. Typical Mass Transfer Processes into water or vice versa to either increase or decrease the
solids concentration of a given system.
Many processes involve criteria other than solids suspen-
Another industrial application is mixing of paper pulp
sion, for example, crystallization, precipitation, and many
and slurries. An entire technology exists for this fluid,
types of leaching and chemical reactions. In crystalliza-
which is quite unique compared to other liquid–solid sys-
tion, the shear rate around the impeller and other mixing
tems. Basically, there is a question of whether to use baf-
variables can affect the rate of nucleation, and can affect
fles, comparison of both top-entering and side-entering
the ultimate particle size. In some cases, the shear rate can
mixers, as well as the very large effect of type of paper
be such that it can break down forces within the solid par-
pulp and the consistency of the paper pulp in the vessel.
ticle and can affect the ultimate particle size and shape.
Other examples include fermentation, in which there is
There are some very fragile precipitate crystals that are
a biological solid producing the desired product, and the
very much affected by the mixer variables.
role of fluid shear rates on the biological solids is a critical
In leaching, there usually is a very rapid leach rate that
consideration as well as the gas–liquid mass transfer (see
occurs when the mineral is on the surface of the particle,
Section VI).
but many times the internal diffusion of the solid through
Another class of applications is the high shear mixers
the solid particle becomes controlling, and mixer vari-
used to break up agglomerates of particles as well as to
ables do not affect the leaching rate beyond that point.
cause rapid dissolving of solids into solvents. A further
In studying the effect of mixing on leaching processes,
type includes the catalytic processes such as hydrogena-
it is normally desirable to run separate experiments with
tion, in which there is a basic gas–liquid mass transfer to
be satisfied, but in addition, effective mixing and shear rate
on the catalyst particle fluid film as well as degradation
must be considered.
IV. GAS–LIQUID CONTACTING
Many times a specification calls for a fluid mixer to pro-
duce a “good dispersion” of so many computational fluid
mixing (CFM), of gas into a given volume of liquid.
Actually, there are very few applications in which dis-
persion of gas–liquid is the ultimate process requirement.
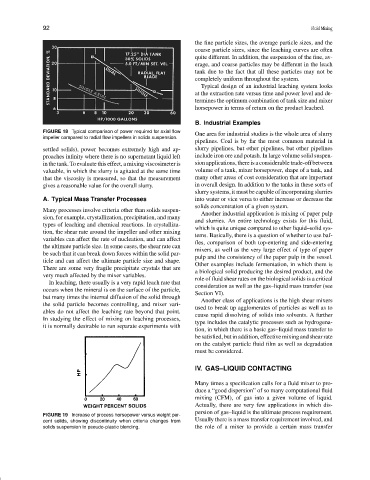
FIGURE 19 Increase of process horsepower versus weight per-
cent solids, showing discontinuity when criteria changes from Usually there is a mass transfer requirement involved, and
solids suspension to pseudo-plastic blending. the role of a mixer to provide a certain mass transfer