Page 135 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 135
P1: FPP Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002C-85 May 17, 2001 20:35
Catalysis, Homogeneous 483
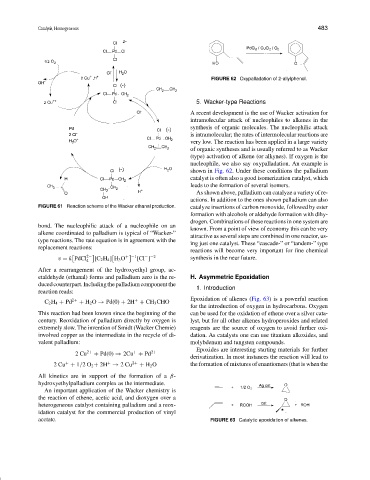
FIGURE 62 Oxypalladation of 2-allylphenol.
5. Wacker-type Reactions
A recent development is the use of Wacker activation for
intramolecular attack of nucleophiles to alkenes in the
synthesis of organic molecules. The nucleophilic attack
is intramolecular; the rates of intermolecular reactions are
very low. The reaction has been applied in a large variety
of organic syntheses and is usually referred to as Wacker
(type) activation of alkene (or alkynes). If oxygen is the
nucleophile, we also say oxypalladation. An example is
shown in Fig. 62. Under these conditions the palladium
catalyst is often also a good isomerization catalyst, which
leads to the formation of several isomers.
As shown above, palladium can catalyze a variety of re-
actions. In addition to the ones shown palladium can also
FIGURE 61 Reaction scheme of the Wacker ethanal production. catalyze insertions of carbon monoxide, followed by ester
formation with alcohols or aldehyde formation with dihy-
drogen. Combinations of these reactions in one system are
bond. The nucleophilic attack of a nucleophile on an
known. From a point of view of economy this can be very
alkene coordinated to palladium is typical of “Wacker-”
attractive as several steps are combined in one reactor, us-
type reactions. The rate equation is in agreement with the
ing just one catalyst. These “cascade-” or “tandem-” type
replacement reactions:
reactions will become very important for fine chemical
+ −1 − −2
v = k PdCl 2− [C 2 H 4 ] H 3 O [Cl ] synthesis in the near future.
4
After a rearrangement of the hydroxyethyl group, ac-
etaldehyde (ethanal) forms and palladium zero is the re- H. Asymmetric Epoxidation
ducedcounterpart.Includingthepalladiumcomponentthe
1. Introduction
reaction reads:
Epoxidation of alkenes (Fig. 63) is a powerful reaction
+
C 2 H 4 + Pd 2+ + H 2 O → Pd(0) + 2H + CH 3 CHO
for the introduction of oxygen in hydrocarbons. Oxygen
This reaction had been known since the beginning of the can be used for the oxidation of ethene over a silver cata-
century. Reoxidation of palladium directly by oxygen is lyst, but for all other alkenes hydroperoxides and related
extremely slow. The invention of Smidt (Wacker Chemie) reagents are the source of oxygen to avoid further oxi-
involved copper as the intermediate in the recycle of di- dation. As catalysts one can use titanium alkoxides, and
valent palladium: molybdenum and tungsten compounds.
Epoxides are interesting starting materials for further
2Cu 2+ + Pd(0) → 2Cu + Pd 2+
+
derivatization. In most instances the reaction will lead to
+
2Cu + 1/2O 2 + 2H → 2Cu 2+ + H 2 O the formation of mixtures of enantiomers (that is when the
+
All kinetics are in support of the formation of a β-
hydroxyethylpalladium complex as the intermediate.
An important application of the Wacker chemistry is
the reaction of ethene, acetic acid, and dioxygen over a
heterogeneous catalyst containing palladium and a reox-
idation catalyst for the commercial production of vinyl
acetate. FIGURE 63 Catalytic epoxidation of alkenes.