Page 218 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 218
P1: GPJ/GLT P2: GQT Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en011-542 July 26, 2001 15:33
504 Organic Chemistry, Synthesis
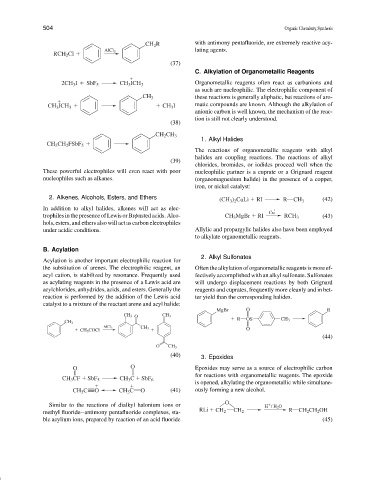
CH 2 R with antimony pentafluoride, are extremely reactive acy-
lating agents.
AlCl 3
RCH 2 Cl
(37)
C. Alkylation of Organometallic Reagents
Organometallic reagents often react as carbanions and
2CH 3 I SbF 5 CH 3 ICH 3
as such are nucleophilic. The electrophilic component of
CH 3 these reactions is generally aliphatic, but reactions of aro-
CH 3 ICH 3 CH 3 I matic compounds are known. Although the alkylation of
anionic carbon is well known, the mechanism of the reac-
tion is still not clearly understood.
(38)
CH 2 CH 3
1. Alkyl Halides
CH 3 CH 2 FSbF 5
The reactions of organometallic reagents with alkyl
halides are coupling reactions. The reactions of alkyl
(39)
chlorides, bromides, or iodides proceed well when the
These powerful electrophiles will even react with poor nucleophilic partner is a cuprate or a Grignard reagent
nucleophiles such as alkanes. (organomagnesium halide) in the presence of a copper,
iron, or nickel catalyst:
2. Alkenes, Alcohols, Esters, and Ethers (CH 3 ) 2 CuLi RI R CH 3 (42)
In addition to alkyl halides, alkenes will act as elec-
Cu
trophiles in the presence of Lewis or Brφnsted acids. Alco- CH 3 MgBr RI RCH 3 (43)
hols, esters, and ethers also will act as carbon electrophiles
under acidic conditions. Allylic and propargylic halides also have been employed
to alkylate organometallic reagents.
B. Acylation
2. Alkyl Sulfonates
Acylation is another important electrophilic reaction for
the substitution of arenes. The electrophilic reagent, an Often the alkylation of organometallic reagents is more ef-
acyl cation, is stabilized by resonance. Frequently used fectively accomplished with an alkyl sulfonate. Sulfonates
as acylating reagents in the presence of a Lewis acid are will undergo displacement reactions by both Grignard
acylchlorides, anhydrides, acids, and esters. Generally the reagents and cuprates, frequently more cleanly and in bet-
reaction is performed by the addition of the Lewis acid ter yield than the corresponding halides.
catalyst to a mixture of the reactant arene and acyl halide:
MgBr O R
CH 3 O CH 3
R OS CH 3
CH 3
AlCl 3 CH 3
CH 3 COCl O
(44)
O CH 3
(40) 3. Epoxides
O O Epoxides may serve as a source of electrophilic carbon
CH 3 CF SbF 5 CH 3 C SbF 6 for reactions with organometallic reagents. The epoxide
is opened, alkylating the organometallic while simultane-
CH 3 C O CH 3 C O (41) ously forming a new alcohol.
Similar to the reactions of dialkyl halonium ions or O H / H 2 O
RLi R CH 2 CH 2 OH
methyl fluoride antimony pentafluoride complexes, sta- CH 2 CH 2
ble acylium ions, prepared by reaction of an acid fluoride (45)