Page 220 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 220
P1: GPJ/GLT P2: GQT Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en011-542 July 26, 2001 15:33
506 Organic Chemistry, Synthesis
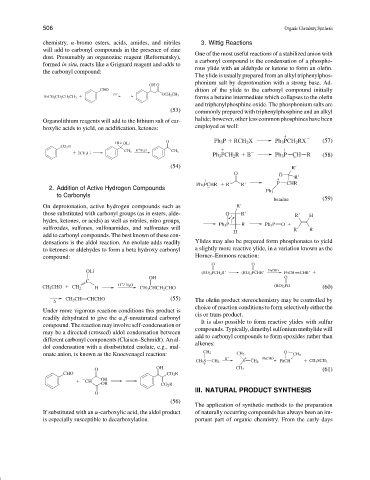
chemistry, α-bromo esters, acids, amides, and nitriles 3. Wittig Reactions
will add to carbonyl compounds in the presence of zinc
One of the most useful reactions of a stabilized anion with
dust. Presumably an organozinc reagent (Reformatsky),
a carbonyl compound is the condensation of a phospho-
formed in situ, reacts like a Grignard reagent and adds to
rous ylide with an aldehyde or ketone to form an olefin.
the carbonyl compound:
The ylide is usually prepared from an alkyl triphenylphos-
phonium salt by deprotonation with a strong base. Ad-
OH O
CHO dition of the ylide to the carbonyl compound initially
BrCH 2 CO 2 CH 2 CH 3 Zn OCH 2 CH 3 forms a betaine intermediate which collapses to the olefin
and triphenylphosphine oxide. The phosphonium salts are
(53) commonly prepared with triphenylphosphine and an alkyl
halide; however, other less common phosphines have been
Organolithium reagents will add to the lithium salt of car-
employed as well:
boxylic acids to yield, on acidification, ketones:
O Ph 3 P RCH 2 X Ph 3 PCH 2 RX (57)
OLi OLi
CO 2 H
H /H 2 O
2CH 3 Li CH 3 CH 3 Ph 3 PCH 2 R B Ph 3 P CH R (58)
_
(54) R
O
O
R
Ph 3 PCHR R R P CHR
2. Addition of Active Hydrogen Compounds
Ph 3
to Carbonyls
betaine (59)
On deprotonation, active hydrogen compounds such as R
those substituted with carbonyl groups (as in esters, alde- O R R H
hydes, ketones, or acids) as well as nitriles, nitro groups,
Ph 3 P R Ph 3 P O
sulfoxides, sulfones, sulfonamides, and sulfonates will R R
H
add to carbonyl compounds. The best known of these con-
densations is the aldol reaction. An enolate adds readily Ylides may also be prepared form phosphonates to yield
to ketones or aldehydes to form a beta hydroxy carbonyl a slightly more reactive ylide, in a variation known as the
compound: Horner–Emmons reaction:
O O
OLi (RO) 2 PCH 2 R (RO) 2 PCHR PhCHO PhCH CHR
OH O
C
CH 3 CHO CH 2 H H / H 2 O CH 3 CHCH 2 CHO (RO) 2 PO (60)
CH 3 CH CHCHO (55)
The olefin product stereochemistry may be controlled by
choice of reaction conditions to form selectively either the
Under more vigorous reaction conditions this product is
cis or trans product.
readily dehydrated to give the α,β-unsaturated carbonyl
It is also possible to form reactive ylides with sulfur
compound. The reaction may involve self-condensation or
compounds. Typically, dimethyl sulfonium methylide will
may be a directed (crossed) aldol condensation between
add to carbonyl compounds to form epoxides rather than
different carbonyl components (Claisen–Schmidt). An al-
alkenes:
dol condensation with a disubstituted enolate, e.g., mal-
onate anion, is known as the Knoevenagel reaction: CH 2 CH 3 O CH 2
PhCHO
B
CH 3 S CH 3 S CH 2 PhCH CH 3 SCH 3
O OH CH 3 (61)
CHO CO 2 R
CH OR CO 2 R
OR
III. NATURAL PRODUCT SYNTHESIS
O
(56)
The application of synthetic methods to the preparation
If substituted with an α-carboxylic acid, the aldol product of naturally occurring compounds has always been an im-
is especially susceptible to decarboxylation. portant part of organic chemistry. From the early days