Page 225 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 225
P1: GPJ/GLT P2: GQT Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en011-542 July 26, 2001 15:33
Organic Chemistry, Synthesis 511
3. Complexed Lithium Aluminum Hydrides
BH 2
Enantioselective reduction of aldehydes and ketones has
(67)
also been possible with lithium aluminum hydride re-
agents complexed in a chiral environment. The lability
of the ligands around lithium aluminum hydride reagents
has so far limited the effectiveness of these reductions. The
2. Chiral Borohydrides
most effective ligands have been those containing at least
The enantiospecific reduction of carbonyl compounds to one nitrogen. N-substituted amino methyl pyrrolidines,
alcohols is an extremely useful reaction. Aldehydes have prepared from proline, have been used in the reduction of
been successfully reduced with chiral trialkylboranes to ketones to give optical yields as high as 96%:
give products with very high optical purity. The hydrob-
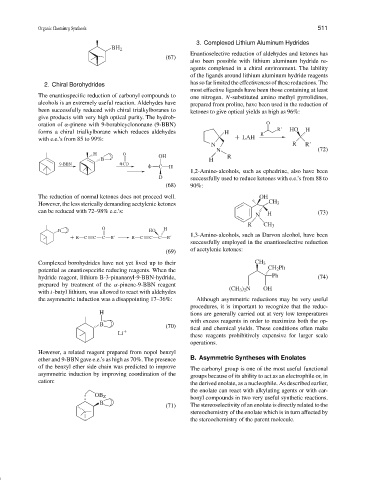
oration of α-pinene with 9-borabicyclononane (9-BBN) O
R HO
forms a chiral trialkylborane which reduces aldehydes H R H
with e.e.’s from 85 to 99%: LAH
N R R
N (72)
H O OH R
B H
9-BBN
CD
C H
1,2-Amino-alcohols, such as ephedrine, also have been
D successfully used to reduce ketones with e.e.’s from 88 to
(68) 90%:
The reduction of normal ketones does not proceed well. OH
However, the less sterically demanding acetylenic ketones CH 3
can be reduced with 72–98% e.e.’s: (73)
N H
R CH 3
O H
B HO
1,3-Amino-alcohols, such as Darvon alcohol, have been
R C C C R R C C C R
successfully employed in the enantioselective reduction
(69) of acetylenic ketones:
Complexed borohydrides have not yet lived up to their CH 3
CH 2 Ph
potential as enantiospecific reducing reagents. When the
hydride reagent, lithium B-3-pinananyl-9-BBN-hydride, Ph (74)
prepared by treatment of the α-pinene-9-BBN reagent
(CH 3 ) 2 N OH
with t-butyl lithium, was allowed to react with aldehydes
the asymmetric induction was a disappointing 17–36%: Although asymmetric reductions may be very useful
procedures, it is important to recognize that the reduc-
H tions are generally carried out at very low temperatures
with excess reagents in order to maximize both the op-
B (70) tical and chemical yields. These conditions often make
Li
these reagents prohibitively expensive for larger scale
operations.
However, a related reagent prepared from nopol benzyl
ether and 9-BBN gave e.e.’s as high as 70%. The presence B. Asymmetric Syntheses with Enolates
of the benzyl ether side chain was predicted to improve The carbonyl group is one of the most useful functional
asymmetric induction by improving coordination of the groups because of its ability to act as an electrophile or, in
cation: the derived enolate, as a nucleophile. As described earlier,
the enolate can react with alkylating agents or with car-
OB Z
bonyl compounds in two very useful synthetic reactions.
B
(71) The stereoselectivity of an enolate is directly related to the
stereochemistry of the enolate which is in turn affected by
the stereochemistry of the parent molecule.