Page 51 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 51
P1: LDK Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN001F-21 May 7, 2001 13:44
490 Alkaloids
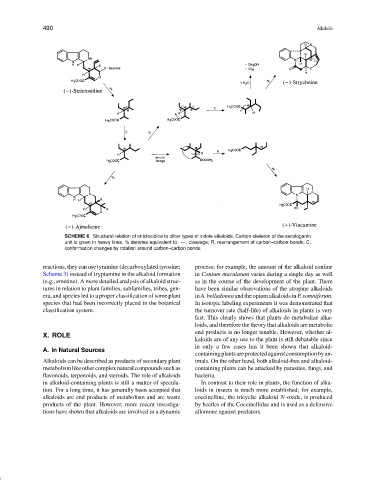
SCHEME 6 Structural relation of strictosidine to other types of indole alkaloids. Carbon skeleton of the secologanin
unit is given in heavy lines. % denotes equivalent to: ∧∧∧, cleavage; R, rearrangement of carbon–carbon bonds; C,
conformation changes by rotation around carbon–carbon bonds.
reactions, they can use tyramine (decarboxylated tyrosine; process; for example, the amount of the alkaloid coniine
Scheme 3) instead of tryptamine in the alkaloid formation in Conium maculatum varies during a single day as well
(e.g., emetine). A more detailed analysis of alkaloid struc- as in the course of the development of the plant. There
tures in relation to plant families, subfamilies, tribes, gen- have been similar observations of the atropine alkaloids
era, and species led to a proper classification of some plant in A. belladonna and the opium alkaloidsin P. somniferum.
species that had been incorrectly placed in the botanical In isotopic labeling experiments it was demonstrated that
classification system. the turnover rate (half-life) of alkaloids in plants is very
fast. This clearly shows that plants do metabolize alka-
loids, and therefore the theory that alkaloids are metabolic
end products is no longer tenable. However, whether al-
X. ROLE
kaloids are of any use to the plant is still debatable since
in only a few cases has it been shown that alkaloid-
A. In Natural Sources
containingplantsareprotectedagainstconsumptionbyan-
Alkaloids can be described as products of secondary plant imals. On the other hand, both alkaloid-free and alkaloid-
metabolism like other complex natural compounds such as containing plants can be attacked by parasites, fungi, and
flavonoids, terpenoids, and steroids. The role of alkaloids bacteria.
in alkaloid-containing plants is still a matter of specula- In contrast to their role in plants, the function of alka-
tion. For a long time, it has generally been accepted that loids in insects is much more established; for example,
alkaloids are end products of metabolism and are waste coccinelline, the tricyclic alkaloid N-oxide, is produced
products of the plant. However, more recent investiga- by beetles of the Coccinellidae and is used as a defensive
tions have shown that alkaloids are involved in a dynamic allomone against predators.