Page 52 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 52
P1: LDK Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN001F-21 May 7, 2001 13:44
Alkaloids 491
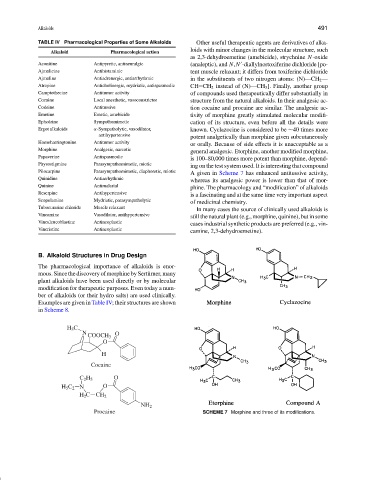
TABLE IV Pharmacological Properties of Some Alkaloids Other useful therapeutic agents are derivatives of alka-
loids with minor changes in the molecular structure, such
Alkaloid Pharmacological action
as 2,3-dehydroemetine (amebicide), strychnine N-oxide
Aconitine Antipyretic, antineuralgic (analeptic), and N,N -diallylnortoxiferine dichloride [po-
Ajmalicine Antihistaminic tent muscle relaxant; it differs from toxiferine dichloride
Ajmaline Antiadrenergic, antiarrhythmic in the substituents of two nitrogen atoms: (N)—CH 2 —
Atropine Anticholinergic, mydriatic, antispasmodic CH CH 2 instead of (N)—CH 3 ]. Finally, another group
Camptothecine Antitumor activity of compounds used therapeutically differ substantially in
Cocaine Local anesthetic, vasoconstrictor structure from the natural alkaloids. In their analgesic ac-
Codeine Antitussive tion cocaine and procaine are similar. The analgesic ac-
Emetine Emetic, amebicide tivity of morphine greatly stimulated molecular modifi-
Ephedrine Sympathomimetic cation of its structure, even before all the details were
Ergot alkaloids α-Sympatholytic, vasodilator, known. Cyclazocine is considered to be ∼40 times more
antihypertensive
potent analgetically than morphine given subcutaneously
Homoharringtonine Antitumor activity
or orally. Because of side effects it is unacceptable as a
Morphine Analgesic, narcotic
general analgesic. Etorphine, another modified morphine,
Papaverine Antispasmodic
is 100–80,000 times more potent than morphine, depend-
Physostigmine Parasympathomimetic, miotic
ing on the test system used. It is interesting that compound
Pilocarpine Parasympathomimetic, diaphoretic, miotic
A given in Scheme 7 has enhanced antitussive activity,
Quinidine Antiarrhythmic
whereas its analgesic power is lower than that of mor-
Quinine Antimalarial
phine. The pharmacology and “modification” of alkaloids
Reserpine Antihypertensive is a fascinating and at the same time very important aspect
Scopolamine Mydriatic, parasympatholytic of medicinal chemistry.
Tubocurarine chloride Muscle relaxant In many cases the source of clinically used alkaloids is
Vincamine Vasodilator, antihypertensive still the natural plant (e.g., morphine, quinine), but in some
Vincaleucoblastine Antineoplastic cases industrial synthetic products are preferred (e.g., vin-
Vincristine Antineoplastic camine, 2,3-dehydroemetine).
B. Alkaloid Structures in Drug Design
The pharmacological importance of alkaloids is enor-
mous. Since the discovery of morphine by Sert¨urner, many
plant alkaloids have been used directly or by molecular
modification for therapeutic purposes. Even today a num-
ber of alkaloids (or their hydro salts) are used clinically.
Examples are given in Table IV; their structures are shown
in Scheme 8.
H 3 C
N O
COOCH 3
O
H
Cocaine
O
C 2 H 5
N O
H 5 C 2
C
H 2 CH 2
NH 2
Procaine SCHEME 7 Morphine and three of its modifications.