Page 49 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 49
P1: LDK Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN001F-21 May 7, 2001 13:44
488 Alkaloids
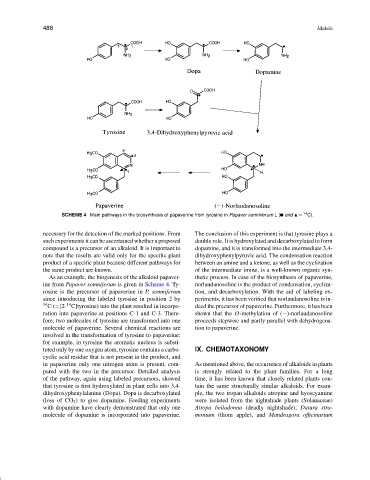
SCHEME 4 Main pathways in the biosynthesis of papaverine from tyrosine in Papaver somniferum L( and = 14 C).
necessary for the detection of the marked positions. From The conclusion of this experiment is that tyrosine plays a
such experiments it can be ascertained whether a proposed double role. It is hydroxylated and decarboxylated to form
compound is a precursor of an alkaloid. It is important to dopamine, and it is transformed into the intermediate 3,4-
note that the results are valid only for the specific plant dihydroxyphenylpyruvic acid. The condensation reaction
product of a specific plant because different pathways for between an amine and a ketone, as well as the cyclization
the same product are known. of the intermediate imine, is a well-known organic syn-
As an example, the biogenesis of the alkaloid papaver- thetic process. In case of the biosynthesis of papaverine,
ine from Papaver somniferum is given in Scheme 4. Ty- norlaudanosoline is the product of condensation, cycliza-
rosine is the precursor of papaverine in P. somniferum tion, and decarboxylation. With the aid of labeling ex-
since introducing the labeled tyrosine in position 2 by periments, it has been verified that norlaudanosoline is in-
14 C(=[2- C]tyrosine) into the plant resulted in incorpo- deed the precursor of papaverine. Furthermore, it has been
14
ration into papaverine at positions C-1 and C-3. There- shown that the O-methylation of (−)-norlaudanosoline
fore, two molecules of tyrosine are transformed into one proceeds stepwise and partly parallel with dehydrogena-
molecule of papaverine. Several chemical reactions are tion to papaverine.
involved in the transformation of tyrosine to papaverine:
for example, in tyrosine the aromatic nucleus is substi-
tuted only by one oxygen atom, tyrosine contains a carbo- IX. CHEMOTAXONOMY
cyclic acid residue that is not present in the product, and
in papaverine only one nitrogen atom is present, com- As mentioned above, the occurrence of alkaloids in plants
pared with the two in the precursor. Detailed analysis is strongly related to the plant families. For a long
of the pathway, again using labeled precursors, showed time, it has been known that closely related plants con-
that tyrosine is first hydroxylated in plant cells into 3,4- tain the same structurally similar alkaloids. For exam-
dihydroxyphenylalanine (Dopa). Dopa is decarboxylated ple, the two tropan alkaloids atropine and hyoscyamine
(loss of CO 2 ) to give dopamine. Feeding experiments were isolated from the nightshade plants (Solanaceae)
with dopamine have clearly demonstrated that only one Atropa beiladonna (deadly nightshade), Datura stra-
molecule of dopamine is incorporated into papaverine. monium (thorn apple), and Mandragora officinarium