Page 18 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 18
P1: GJB Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology En001f25 May 7, 2001 13:58
Analytical Chemistry 557
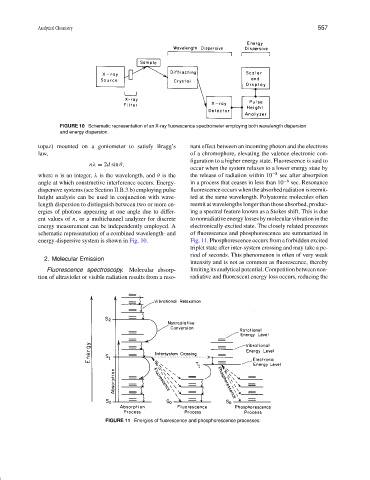
FIGURE 10 Schematic representation of an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer employing both wavelength dispersion
and energy dispersion.
topaz) mounted on a goniometer to satisfy Bragg’s nant effect between an incoming photon and the electrons
law, of a chromophore, elevating the valence electronic con-
figuration to a higher energy state. Fluorescence is said to
nλ = 2d sin θ,
occur when the system relaxes to a lower energy state by
where n is an integer, λ is the wavelength, and θ is the the release of radiation within 10 −8 sec after absorption
angle at which constructive interference occurs. Energy- in a process that ceases in less than 10 −6 sec. Resonance
dispersive systems (see Section II.B.3.b) employing pulse fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is reemit-
height analysis can be used in conjunction with wave- ted at the same wavelength. Polyatomic molecules often
length dispersion to distinguish between two or more en- reemit at wavelengths longer than those absorbed, produc-
ergies of photons appearing at one angle due to differ- ing a spectral feature known as a Stokes shift. This is due
ent values of n, or a multichannel analyzer for discrete to nonradiative energy losses by molecular vibration in the
energy measurement can be independently employed. A electronically excited state. The closely related processes
schematic representation of a combined wavelength- and of fluorescence and phosphorescence are summarized in
energy-dispersive system is shown in Fig. 10. Fig. 11. Phosphorescence occurs from a forbidden excited
triplet state after inter-system crossing and may take a pe-
riod of seconds. This phenomenon is often of very weak
2. Molecular Emission
intensity and is not as common as fluorescence, thereby
Fluorescence spectroscopy. Molecular absorp- limitingitsanalyticalpotential.Competitionbetweennon-
tion of ultraviolet or visible radiation results from a reso- radiative and fluorescent energy loss occurs, reducing the
FIGURE 11 Energies of fluorescence and phosphorescence processes.