Page 227 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 227
P1: ZCK/MBQ P2: GQT Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN008B-382 June 30, 2001 18:58
694 Liquid Chromatography
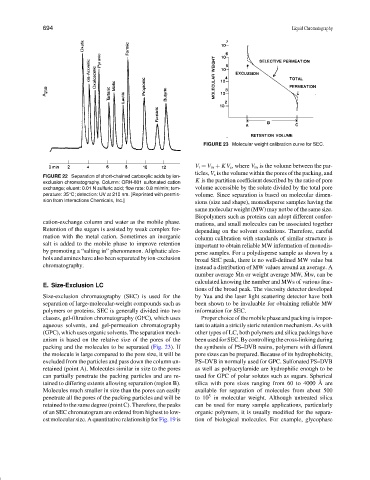
FIGURE 23 Molecular weight calibration curve for SEC.
V r = V m + KV s , where V m is the volume between the par-
ticles, V s is the volume within the pores of the packing, and
FIGURE 22 Separation of short-chained carboxylic acids by ion-
K is the partition coefficient described by the ratio of pore
exclusion chromatography. Column: ORH-801 sulfonated cation
exchange; eluent: 0.01 N sulfuric acid; flow rate: 0.8 ml/min; tem- volume accessible by the solute divided by the total pore
◦
perature: 35 C; detection: UV at 210 nm. [Reprinted with permis- volume. Since separation is based on molecular dimen-
sion from Interactions Chemicals, Inc.]
sions (size and shape), monodisperse samples having the
same molecular weight (MW) may not be of the same size.
Biopolymers such as proteins can adopt different confor-
cation-exchange column and water as the mobile phase. mations, and small molecules can be associated together
Retention of the sugars is assisted by weak complex for- depending on the solvent conditions. Therefore, careful
mation with the metal cation. Sometimes an inorganic column calibration with standards of similar structure is
salt is added to the mobile phase to improve retention important to obtain reliable MW information of monodis-
by promoting a “salting in” phenomenon. Aliphatic alco- perse samples. For a polydisperse sample as shown by a
hols and amines have also been separated by ion-exclusion broad SEC peak, there is no well-defined MW value but
chromatography. instead a distribution of MW values around an average. A
¯
¯
number average Mn or weight average MW, Mw, can be
calculated knowing the number and MWs of various frac-
E. Size-Exclusion LC
tions of the broad peak. The viscosity detector developed
Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) is used for the by Yau and the laser light scattering detector have both
separation of large-molecular-weight compounds such as been shown to be invaluable for obtaining reliable MW
polymers or proteins. SEC is generally divided into two information for SEC.
classes, gel-filtration chromatography (GFC), which uses Proper choice of the mobile phase and packing is impor-
aqueous solvents, and gel-permeation chromatography tant to attain a strictly steric retention mechanism. As with
(GPC), which uses organic solvents. The separation mech- other types of LC, both polymers and silica packings have
anism is based on the relative size of the pores of the been used for SEC. By controlling the cross-linking during
packing and the molecules to be separated (Fig. 23). If the synthesis of PS–DVB resins, polymers with different
the molecule is large compared to the pore size, it will be pore sizes can be prepared. Because of its hydrophobicity,
excluded from the particles and pass down the column un- PS–DVB in normally used for GPC. Sulfonated PS–DVB
retained (point A). Molecules similar in size to the pores as well as polyacrylamide are hydrophilic enough to be
can partially penetrate the packing particles and are re- used for GPC of polar solutes such as sugars. Spherical
˚
tained to differing extents allowing separation (region B). silica with pore sizes ranging from 60 to 4000 A are
Molecules much smaller in size than the pores can easily available for separation of molecules from about 500
5
penetrate all the pores of the packing particles and will be to 10 in molecular weight. Although untreated silica
retained to the same degree (point C). Therefore, the peaks can be used for many sample applications, particularly
of an SEC chromatogram are ordered from highest to low- organic polymers, it is usually modified for the separa-
estmolecularsize.AquantitativerelationshipforFig.19is tion of biological molecules. For example, glycophase