Page 223 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 223
P1: ZCK/MBQ P2: GQT Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN008B-382 June 30, 2001 18:58
690 Liquid Chromatography
replace the typical methanol or acetonitrile modifier. One
advantage of micellar liquid chromatography is in gradient
elution where the reequilibration time can be dramatically
shortened compared to gradient reversed-phase LC. In ad-
dition, direct injection of serum samples for drug analysis
can be tolerated by the HPLC column if a micellar mobile
phase is used.
In general, reversed-phase columns often have only a
shortlifetimewhenusedfortheanalysisofdrugsamplesin
serum, due to the buildup of proteinaceous material on the
hydrophobic particle surface. To overcome this problem,
Pinkerton and co-workers developed the internal surface
reversed-phase class of packings. This material is synthe-
sized by first bonding a hydrophobic polypeptide contain-
ing phenylalanine to the silica surface and inside the pores.
Using the enzyme carboxypeptidase A, the phenylalanine
groups on the surface are cleaved off, but stearic hin-
drance prevents any reaction inside the pores. The small
drug molecules such as phenobarbital can be still retained
chromatographically inside the pores while the protein has
little affinity to the surface hydrophilic phase. Recently,
modifications of this concept have been directed to at-
tachment of a hydrophilic polymer on the outside surface
of the reversed-phase particles to prevent adsorption of
proteins. These packings are sometimes called restricted
access media (RAM).
Hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) is a
type of reversed-phase LC using relatively hydrophilic
column packings and a high-salt content in the mobile
phase. A dedicated HPLC instrument with titanium pump
heads, a special injector, and plastic column hardware
with PEEK connecting tubing is recommended to prevent
corrosion and delecterious sample interactions caused by
stainless steel. Because HIC packings have 10–100 times
less density of hydrophobic groups, a high-salt concen-
tration is necessary to enhance the hydrophobic retention.
Because proteins retain their native conformation in such
mobile phases, HIC is particularly useful for the sepa-
ration of enzymes without denaturation. Typical experi-
mental conditions are the use of a salt gradient from 2 to
0.1 M (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , using a propyl or phenyl column for
the purification of trypsin with high activity.
Because of the great interest in aqueous samples, a
wide variety of reversed-phase HPLC applications have
been published. The pharmaceutical, biochemical, food
and beverage, and the environmental laboratories repre-
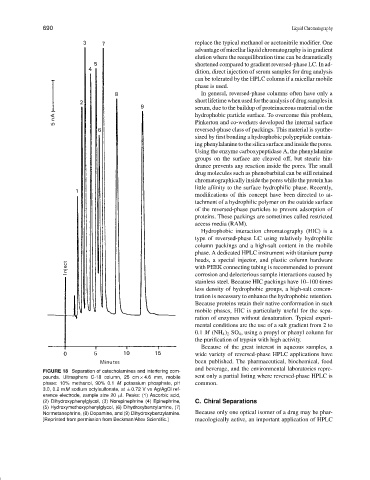
FIGURE 18 Separation of catecholamines and interfering com-
pounds. Ultrasphere C-18 column, 25 cm × 4.6 mm, mobile sent only a partial listing where reversed-phase HPLC is
phase: 10% methanol, 90% 0.1 M potassium phosphate, pH common.
3.0, 0.2 mM sodium octylsulfonate, at ± 0.72 V vs Ag/AgCl ref-
erence electrode, sample size 20 µl. Peaks: (1) Ascorbic acid,
(2) Dihydroxyphenylglycol, (3) Norepinephrine (4) Epinephrine, C. Chiral Separations
(5) Hydroxymethoxyphenylglycol, (6) Dihydroxybenzylamine, (7)
Normetanephrine, (8) Dopamine, and (9) Dihydroxybenzylamine. Because only one optical isomer of a drug may be phar-
[Reprinted from permission from Beckman/Altex Scientific.] macologically active, an important application of HPLC