Page 28 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 28
P1: ZCK Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN005G-231 June 15, 2001 20:46
Enzyme Mechanisms 635
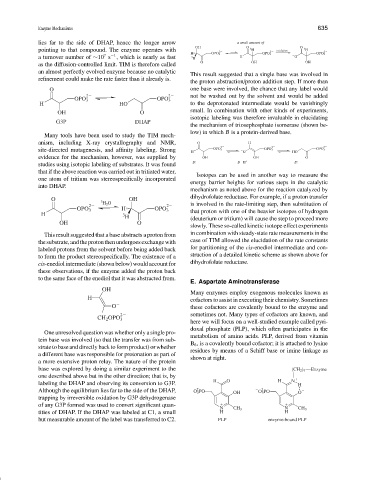
lies far to the side of DHAP, hence the longer arrow a small amount of
pointing to that compound. The enzyme operates with OH O 3 H oxidation O 3 H
H OPO 3 2 OPO 3 2 OPO 3 2
7
−1
a turnover number of ∼10 s , which is nearly as fast 3 H H O
as the diffusion-controlled limit. TIM is therefore called O OH OH
an almost perfectly evolved enzyme because no catalytic
This result suggested that a single base was involved in
refinement could make the rate faster than it already is.
the proton abstraction/proton addition step. If more than
O one base were involved, the chance that any label would
2 2 not be washed out by the solvent and would be added
OPO 3 OPO 3
H HO to the deprotonated intermediate would be vanishingly
small. In combination with other kinds of experiments,
OH O
isotopic labeling was therefore invaluable in elucidating
G3P DHAP
the mechanism of triosephosphate isomerase (shown be-
low) in which B is a protein-derived base.
Many tools have been used to study the TIM mech-
anism, including X-ray crystallography and NMR, O H
2 2 2
site-directed mutagenesis, and affinity labeling. Strong OPO 3 OPO 3 OPO 3
H O HO
evidence for the mechanism, however, was supplied by OH OH O
B
B H
B
studies using isotopic labeling of substrates. It was found
that if the above reaction was carried out in tritiated water,
Isotopes can be used in another way to measure the
one atom of tritium was stereospecifically incorporated
energy barrier heights for various steps in the catalytic
into DHAP.
mechanism as noted above for the reaction catalyzed by
dihydrofolate reductase. For example, if a proton transfer
O 3 H 2 O OH
2 2 is involved in the rate-limiting step, then substitution of
OPO 3 H OPO 3 that proton with one of the heavier isotopes of hydrogen
H 3
H (deuterium or tritium) will cause the step to proceed more
OH O
slowly. These so-called kinetic isotope effect experiments
This result suggested that a base abstracts a proton from in combination with steady-state rate measurements in the
thesubstrate,andtheprotonthenundergoesexchangewith case of TIM allowed the elucidation of the rate constants
labeled protons from the solvent before being added back for partitioning of the cis-enediol intermediate and con-
to form the product stereospecifically. The existence of a struction of a detailed kinetic scheme as shown above for
cis-enediol intermediate (shown below) would account for dihydrofolate reductase.
these observations, if the enzyme added the proton back
to the same face of the enediol that it was abstracted from.
E. Aspartate Aminotransferase
OH
Many enzymes employ exogenous molecules known as
H
cofactors to assist in executing their chemistry. Sometimes
O these cofactors are covalently bound to the enzyme and
2 sometimes not. Many types of cofactors are known, and
CH 2 OPO 3
here we will focus on a well-studied example called pyri-
doxal phosphate (PLP), which often participates in the
One unresolved question was whether only a single pro-
metabolism of amino acids. PLP, derived from vitamin
tein base was involved (so that the transfer was from sub-
B 6 , is a covalently bound cofactor; it is attached to lysine
strate to base and directly back to form product) or whether
residues by means of a Schiff base or imine linkage as
a different base was responsible for protonation as part of
shown at right.
a more extensive proton relay. The nature of the protein
base was explored by doing a similar experiment to the (CH 2 ) 4 Enzyme
one described above but in the other direction; that is, by
labeling the DHAP and observing its conversion to G3P. H O H N H
Although the equilibrium lies far to the side of the DHAP, 2 OH 2 O
O 3 PO
O 3 PO
trapping by irreversible oxidation by G3P dehydrogenase
of any G3P formed was used to convert significant quan-
N CH 3 N CH 3
tities of DHAP. If the DHAP was labeled at C1, a small H H
but measurable amount of the label was transferred to C2. PLP enzyme-bound PLP