Page 130 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 130
P1: FMX/LSU P2: GPB/GRD P3: GLQ Final pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN012c-593 July 26, 2001 15:56
636 Polymer Processing
The production of manmade fibers usually includes the
following processes:
1. Preparation of polymer (polymerization, chemical
modification, etc.)
2. Preparation of the spinning fluid (polymer melt or
solution)
3. Spinning (extrusion, solidification, and deformation
of the spinning line or filament)
4. Drawing (due to a higher linear speed at the take-up
roll relative to that at the die; drawing is used to
increase the degree of molecular orientation and
improve the tensile strength, modulus of elasticity
and elongation of the fibers)
5. Heat treatment
6. Textile processing (twisting, oiling, dyeing, etc.).
The spinning process can be achieved mainly by three
procedures: melt spinning, solution dry-spinning, and so-
lution wet-spinning. Of these three procedures, melt spin-
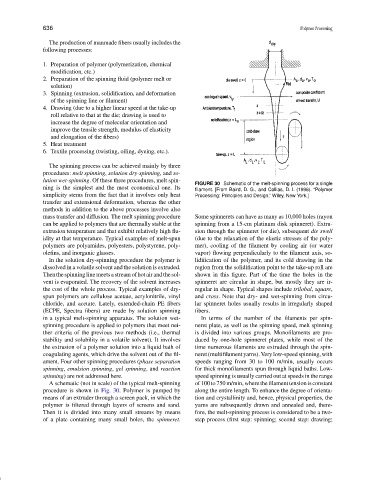
FIGURE 30 Schematic of the melt-spinning process for a single
ning is the simplest and the most economical one. Its filament. [From Baird, D. G., and Collias, D. I. (1998). “Polymer
simplicity stems from the fact that it involves only heat Processing: Principles and Design,” Wiley, New York.]
transfer and extensional deformation, whereas the other
methods in addition to the above processes involve also
mass transfer and diffusion. The melt spinning procedure Some spinnerets can have as many as 10,000 holes (rayon
can be applied to polymers that are thermally stable at the spinning from a 15-cm platinum disk spinneret). Extru-
extrusion temperature and that exhibit relatively high flu- sion through the spinneret (or die), subsequent die swell
idity at that temperature. Typical examples of melt-spun (due to the relaxation of the elastic stresses of the poly-
polymers are polyamides, polyesters, polystyrene, poly- mer), cooling of the filament by cooling air (or water
olefins, and inorganic glasses. vapor) flowing perpendicularly to the filament axis, so-
In the solution dry-spinning procedure the polymer is lidification of the polymer, and its cold drawing in the
dissolved in a volatile solvent and the solution is extruded. region from the solidification point to the take-up roll are
Then the spinning line meets a stream of hot air and the sol- shown in this figure. Part of the time the holes in the
vent is evaporated. The recovery of the solvent increases spinneret are circular in shape, but mostly they are ir-
the cost of the whole process. Typical examples of dry- regular in shape. Typical shapes include trilobal, square,
spun polymers are cellulose acetate, acrylonitrile, vinyl and cross. Note that dry- and wet-spinning from circu-
chloride, and acetate. Lately, extended-chain PE fibers lar spinneret holes usually results in irregularly shaped
(ECPE, Spectra fibers) are made by solution spinning fibers.
in a typical melt-spinning apparatus. The solution wet- In terms of the number of the filaments per spin-
spinning procedure is applied to polymers that meet nei- neret plate, as well as the spinning speed, melt spinning
ther criteria of the previous two methods (i.e., thermal is divided into various groups. Monofilaments are pro-
stability and solubility in a volatile solvent). It involves duced by one-hole spinneret plates, while most of the
the extrusion of a polymer solution into a liquid bath of time numerous filaments are extruded through the spin-
coagulating agents, which drive the solvent out of the fil- neret(multifilamentyarns).Verylow-speedspinning,with
ament. Four other spinning procedures (phase separation speeds ranging from 30 to 100 m/min, usually occurs
spinning, emulsion spinning, gel spinning, and reaction for thick monofilaments spun through liquid baths. Low-
spinning) are not addressed here. speed spinning is usually carried out at speeds in the range
A schematic (not in scale) of the typical melt-spinning of100to750m/min,wherethe filamenttensionisconstant
procedure is shown in Fig. 30. Polymer is pumped by along the entire length. To enhance the degree of orienta-
means of an extruder through a screen pack, in which the tion and crystallinity and, hence, physical properties, the
polymer is filtered through layers of screens and sand. yarns are subsequently drawn and annealed and, there-
Then it is divided into many small streams by means fore, the melt-spinning process is considered to be a two-
of a plate containing many small holes, the spinneret. step process (first step: spinning; second step: drawing;