Page 129 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 129
P1: FMX/LSU P2: GPB/GRD P3: GLQ Final pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN012c-593 July 26, 2001 15:56
Polymer Processing 635
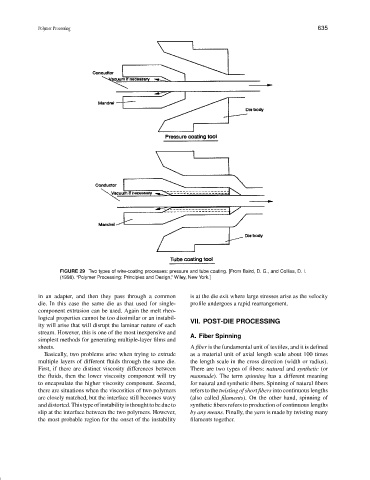
FIGURE 29 Two types of wire-coating processes: pressure and tube coating. [From Baird, D. G., and Collias, D. I.
(1998). “Polymer Processing: Principles and Design,” Wiley, New York.]
in an adapter, and then they pass through a common is at the die exit where large stresses arise as the velocity
die. In this case the same die as that used for single- profile undergoes a rapid rearrangement.
component extrusion can be used. Again the melt rheo-
logical properties cannot be too dissimilar or an instabil- VII. POST-DIE PROCESSING
ity will arise that will disrupt the laminar nature of each
stream. However, this is one of the most inexpensive and
A. Fiber Spinning
simplest methods for generating multiple-layer films and
sheets. A fiber is the fundamental unit of textiles, and it is defined
Basically, two problems arise when trying to extrude as a material unit of axial length scale about 100 times
multiple layers of different fluids through the same die. the length scale in the cross direction (width or radius).
First, if there are distinct viscosity differences between There are two types of fibers: natural and synthetic (or
the fluids, then the lower viscosity component will try manmade). The term spinning has a different meaning
to encapsulate the higher viscosity component. Second, for natural and synthetic fibers. Spinning of natural fibers
there are situations when the viscosities of two polymers refers to the twisting of short fibers into continuous lengths
are closely matched, but the interface still becomes wavy (also called filaments). On the other hand, spinning of
anddistorted.Thistypeofinstabilityisthoughttobedueto synthetic fibers refers to production of continuous lengths
slip at the interface between the two polymers. However, by any means. Finally, the yarn is made by twisting many
the most probable region for the onset of the instability filaments together.