Page 224 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 224
P1: GOJ/GOI/LCC/HAR P2: GOJ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en012K-946 July 26, 2001 11:14
Polymers, Photoresponsive 733
FIGURE 13 Structural representation of the polyphthalaldehyde
acid-induced depolymerization mechanism.
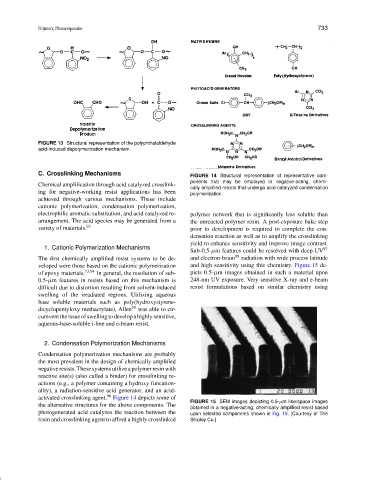
C. Crosslinking Mechanisms FIGURE 14 Structural representation of representative com-
ponents that may be employed in negative-acting, chemi-
Chemical amplification through acid catalyzed crosslink-
cally amplified resists that undergo acid-catalyzed condensation
ing for negative-working resist applications has been polymerization.
achieved through various mechanisms. These include
cationic polymerization, condensation polymerization,
electrophilic aromatic substitution, and acid catalyzed re- polymer network that is significantly less soluble than
arrangement. The acid species may be generated from a the unreacted polymer resin. A post-exposure bake step
variety of materials. 93 prior to development is required to complete the con-
densation reaction as well as to amplify the crosslinking
yield to enhance sensitivity and improve image contrast.
1. Cationic Polymerization Mechanisms 97
Sub-0.5-µm features could be resolved with deep-UV
The first chemically amplified resist systems to be de- and electron-beam 98 radiation with wide process latitude
veloped were those based on the cationic polymerization and high sensitivity using this chemistry. Figure 15 de-
of epoxy materials. 73,94 In general, the resolution of sub- picts 0.5-µm images obtained in such a material upon
0.5-µm features in resists based on this mechanism is 248-nm UV exposure. Very sensitive X-ray and e-beam
difficult due to distortion resulting from solvent-induced resist formulations based on similar chemistry using
swelling of the irradiated regions. Utilizing aqueous
base soluble materials such as poly(hydroxystyrene-
dicyclopentyloxy methacrylate), Allen 95 was able to cir-
cumventtheissueofswellingtodevelopahighlysensitive,
aqueous-base-soluble i-line and e-beam resist.
2. Condensation Polymerization Mechanisms
Condensation polymerization mechanisms are probably
the most prevalent in the design of chemically amplified
negativeresists.Thesesystemsutilizeapolymerresinwith
reactive site(s) (also called a binder) for crosslinking re-
actions (e.g., a polymer containing a hydroxy funcation-
ality), a radiation-sensitive acid generator, and an acid-
activated crosslinking agent. 96 Figure 14 depicts some of
FIGURE 15 SEM images depicting 0.5-µm line/space images
the alternative structures for the above components. The
obtained in a negative-acting, chemically amplified resist based
photogenerated acid catalyzes the reaction between the upon selected components shown in Fig. 15. [Courtesy of The
resin and crosslinking agent to afford a highly crosslinked Shipley Co.]