Page 226 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 226
P1: GOJ/GOI/LCC/HAR P2: GOJ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en012K-946 July 26, 2001 11:14
Polymers, Photoresponsive 735
FIGURE 17 Schematic representation of alternative synthetic
routes to preparing alicyclic polymers.
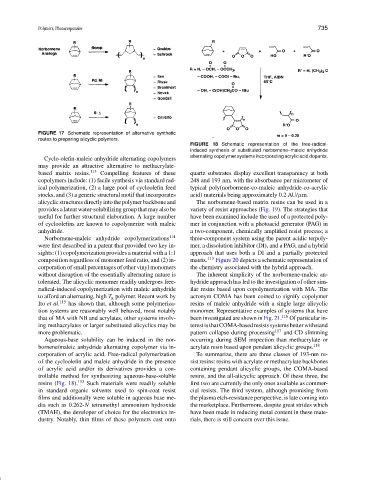
FIGURE 18 Schematic representation of the free-radical-
induced synthesis of substituted norbornene–maleic anhydride
alternating copolymer systems incorporating acrylic acid dopants.
Cyclo-olefin-maleic anhydride alternating copolymers
may provide an attractive alternative to methacrylate-
based matrix resins. 113 Compelling features of these quartz substrates display excellent transparency at both
copolymers include: (1) facile synthesis via standard rad- 248 and 193 nm, with the absorbance per micrometer of
ical polymerization, (2) a large pool of cycloolefin feed typical poly(norbornene-co-maleic anhydride-co-acrylic
stocks, and (3) a generic structural motif that incorporates acid) materials being approximately 0.2 AU/µm.
alicyclic structures directly into the polymer backbone and The norbornene-based matrix resins can be used in a
provides a latent water-solubilizing group that may also be variety of resist approaches (Fig. 19). The strategies that
useful for further structural elaboration. A large number have been examined include the used of a protected poly-
of cycloolefins are known to copolymerize with maleic mer in conjunction with a photoacid generator (PAG) in
anhydride. a two-component, chemically amplified resist process; a
Norbornene-maleic anhydride copolymerizations 114 three-component system using the parent acidic terpoly-
were first described in a patent that provided two key in- mer, a dissolution inhibitor (DI), and a PAG; and a hybrid
sights: (1) copolymerization provides a material with a 1:1 approach that uses both a DI and a partially protected
composition regardless of monomer feed ratio, and (2) in- matrix. 113 Figure 20 depicts a schematic representation of
corporation of small percentages of other vinyl monomers the chemistry associated with the hybrid approach.
without disruption of the essentially alternating nature is The inherent simplicity of the norbornene-maleic an-
tolerated. The alicyclic monomer readily undergoes free- hydride approach has led to the investigation of other sim-
radical-induced copolymerization with maleic anhydride ilar resins based upon copolymerization with MA. The
to afford an alternating, high T g polymer. Recent work by acronym COMA has been coined to signify copolymer
Ito et al. 115 has shown that, although some polymeriza- resins of maleic anhydride with a single large alicyclic
tion systems are reasonably well behaved, most notably monomer. Representative examples of systems that have
that of MA with NB and acrylates, other systems involv- been investigated are shown in Fig. 21. 116 Of particular in-
ing methacrylates or larger substituted alicyclics may be terestisthatCOMA-basedresistssystemsbetterwithstand
more problematic. pattern collapse during processing 117 and CD slimming
Aqueous-base solubility can be induced in the nor- occurring during SEM inspection than methacrylate or
bornene/maleic anhydride alternating copolymer via in- acrylate resin based upon pendant alicyclic groups. 118
corporation of acrylic acid. Free-radical polymerization To summarize, there are three classes of 193-nm re-
of the cycloolefin and maleic anhydride in the presence sist resins: resins with acrylate or methacrylate backbones
of acrylic acid and/or its derivatives provides a con- containing pendant alicyclic groups, the COMA-based
trollable method for synthesizing aqueous-base-soluble resins, and the all-alicyclic approach. Of these three, the
resins (Fig. 18). 113 Such materials were readily soluble first two are currently the only ones available as commer-
in standard organic solvents used to spin-coat resist cial resists. The third system, although promising from
films and additionally were soluble in aqueous base me- the plasma etch-resistance perspective, is late coming into
dia such as 0.262-N tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide the marketplace. Furthermore, despite great strides which
(TMAH), the developer of choice for the electronics in- have been made in reducing metal content in these mate-
dustry. Notably, thin films of these polymers cast onto rials, there is still concern over this issue.