Page 227 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 227
P1: GOJ/GOI/LCC/HAR P2: GOJ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en012K-946 July 26, 2001 11:14
736 Polymers, Photoresponsive
ing rise to high contrast. 120 The oligomeric dissolution in-
hibitors are very soluble in norbornene-maleic anhydride-
acrylate (NB/MA/AA) polymers and exhibit no tendency
towards phase separation at loadings even as high as
40 wt%. Recent work has shown that the blendability
of cholate DIs in general improves with increasing car-
boxylic content of the resin. 121 Generally, the oligomeric
inhibitors improved not only the contrast and solubility of
the exposed areas in 0.262-N TMAH, but also reduced the
unexposed film loss. The optimum adhesion and contrast
were obtained by using a mixture of oligomeric DI with a
polar “monomeric” material such as t-butyl cholate. Re-
cently, a detailed study of the dissolution inhibiton and
promotion capability of a wide range of tert-butyl car-
boxylates derivatives in a p(NB/MA/AA) resin was car-
ried out. 121 It has been found that increasing hydropho-
bicity increased dissolution inhibition ability. The highest
dissolution inhibition was found to occur for hydropho-
bic steroidal carboxylates having largest van der Waals
surfaces for interaction with the polymer matrix. Dissolu-
tion promotion tracked with the number of carboxylic acid
moieties and the hydrophobicity of carboxylic acid moi-
eties released upon acidolytic cleavage of the tert-butyl
carboxylate. Knowing the relative dissolution inhibition
for tert-butyl carboxylates and promotion for carboxylic
acids measured for a p(NB/MA/AA) matrix it was possi-
ble to predict trends in both contrast and maximum rate
of dissolution measured in a p(NB/MA/TBA/AA) (TBA,
tert-butyl acrylate) based resin.
C. Photoacid Generator Design Issues
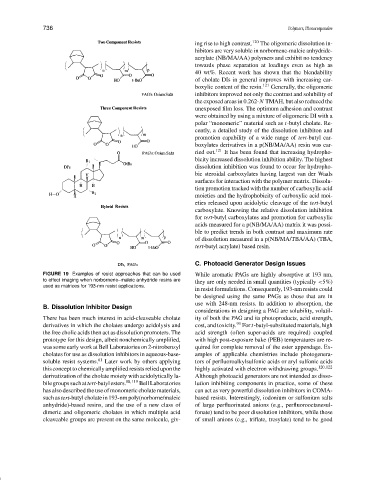
FIGURE 19 Examples of resist approaches that can be used While aromatic PAGs are highly absorptive at 193 nm,
to effect imaging when norbornene–maleic anhydride resins are
they are only needed in small quantities (typically <5%)
used as matrices for 193-nm resist applications.
in resist formulations. Consequently, 193-nm resists could
be designed using the same PAGs as those that are in
use with 248-nm resists. In addition to absorption, the
B. Dissolution Inhibitor Design
considerations in designing a PAG are solubility, volatil-
There has been much interest in acid-cleaveable cholate ity of both the PAG and its photoproducts, acid strength,
93
derivatives in which the cholates undergo acidolysis and cost, and toxicity. For t-butyl-substituted materials, high
the free cholic acids then act as dissolution promoters. The acid strength (often super-acids are required) coupled
prototype for this design, albeit nonchemically amplified, with high post-exposure bake (PEB) temperatures are re-
was some early work at Bell Laboratories on 2-nitrobenzyl quired for complete removal of the ester appendage. Ex-
cholates for use as dissolution inhibitors in aqueous-base- amples of applicable chemistries include photogenera-
soluble resist systems. 61 Later work by others applying tors of perfluoroalkylsulfonic acids or aryl sulfonic acids
this concept to chemically amplified resists relied upon the highly activated with electron withdrawing groups. 120,122
derivatization of the cholate moiety with acidolytically la- Although photoacid generators are not intended as disso-
bilegroupssuchattert-butylesters. 88,119 BellLaboratories lution inhibiting components in practice, some of these
has also described the use of monomeric cholate materials, can act as very powerful dissolution inhibitors in COMA-
such as tert-butyl cholate in 193-nm poly(norborne/maleic based resists. Interestingly, iodonium or sulfonium salts
anhydride)-based resins, and the use of a new class of of large perfluorinated anions (e.g., perfluorooctanesul-
dimeric and oligomeric cholates in which multiple acid fonate) tend to be poor dissolution inhibitors, while those
cleaveable groups are present on the same molecule, giv- of small anions (e.g., triflate, tresylate) tend to be good