Page 228 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 228
P1: GOJ/GOI/LCC/HAR P2: GOJ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en012K-946 July 26, 2001 11:14
Polymers, Photoresponsive 737
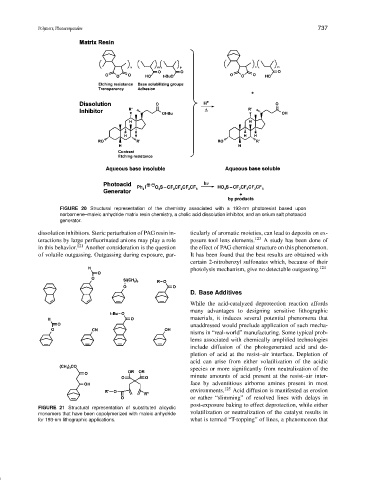
FIGURE 20 Structural representation of the chemistry associated with a 193-nm photoresist based upon
norbornene–maleic anhydride matrix resin chemistry, a cholic acid dissolution inhibitor, and an onium salt photoacid
generator.
dissolution inhibitors. Steric perturbation of PAG resin in- ticularly of aromatic moieties, can lead to deposits on ex-
teractions by large perfluorinated anions may play a role posure tool lens elements. 123 A study has been done of
in this behavior. 121 Another consideration is the question the effect of PAG chemical structure on this phenomenon.
of volatile outgassing. Outgassing during exposure, par- It has been found that the best results are obtained with
certain 2-nitrobenzyl sulfonates which, because of their
photolysis mechanism, give no detectable outgassing. 124
D. Base Additives
While the acid-catalyzed deprotection reaction affords
many advantages to designing sensitive lithographic
materials, it induces several potential phenomena that
unaddressed would preclude application of such mecha-
nisms in “real-world” manufacturing. Some typical prob-
lems associated with chemically amplified technologies
include diffusion of the photogenerated acid and de-
pletion of acid at the resist–air interface. Depletion of
acid can arise from either volatilization of the acidic
species or more significantly from neutralization of the
minute amounts of acid present at the resist–air inter-
face by adventitious airborne amines present in most
environments. 125 Acid diffusion is manifested as erosion
or rather “slimming” of resolved lines with delays in
post-exposure baking to effect deprotection, while either
FIGURE 21 Structural representation of substituted alicyclic
monomers that have been copolymerized with maleic anhydride volatilization or neutralization of the catalyst results in
for 193-nm lithographic applications. what is termed “T-topping” of lines, a phenomenon that