Page 292 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 292
P1: GNH Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009M-428 July 18, 2001 1:6
Metal Particles and Cluster Compounds 549
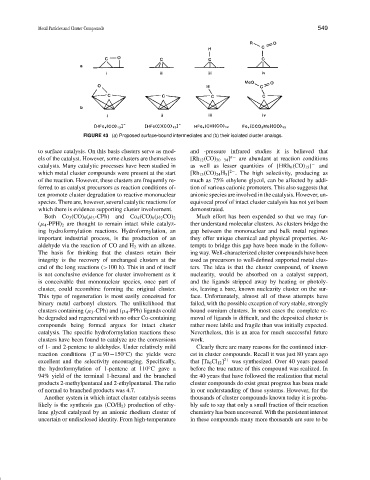
FIGURE 43 (a) Proposed surface-bound intermediates and (b) their isolated cluster analogs.
to surface catalysis. On this basis clusters serve as mod- and -pressure infrared studies it is believed that
els of the catalyst. However, some clusters are themselves [Rh 12 (CO) 30−34 ] n− are abundant at reaction conditions
catalysts. Many catalytic processes have been studied in as well as lesser quantities of [HRh 6 (CO) 15 ] − and
2−
which metal cluster compounds were present at the start [Rh 13 (CO) 24 H 3 ] . The high selectivity, producing as
of the reaction. However, these clusters are frequently re- much as 75% ethylene glycol, can be affected by addi-
ferred to as catalyst precursors as reaction conditions of- tion of various cationic promoters. This also suggests that
ten promote cluster degradation to reactive mononuclear anionic species are involved in the catalysis. However, un-
species. There are, however, several catalytic reactions for equivocal proof of intact cluster catalysis has not yet been
which there is evidence supporting cluster involvement. demonstrated.
Both Co 3 (CO) 9 (µ 3 -CPh) and Co 4 (CO) 8 (µ 2 CO) 2 Much effort has been expended so that we may fur-
(µ 4 -PPH) 2 are thought to remain intact while catalyz- ther understand molecular clusters. As clusters bridge the
ing hydroformylation reactions. Hydroformylation, an gap between the mononuclear and bulk metal regimes
important industrial process, is the production of an they offer unique chemical and physical properties. At-
aldehyde via the reaction of CO and H 2 with an alkene. tempts to bridge this gap have been made in the follow-
The basis for thinking that the clusters retain their ing way. Well-characterized cluster compounds have been
integrity is the recovery of unchanged clusters at the used as precursors to well-defined supported metal clus-
end of the long reactions (>100 h). This in and of itself ters. The idea is that the cluster compound, of known
is not conclusive evidence for cluster involvement as it nuclearity, would be absorbed on a catalyst support,
is conceivable that mononuclear species, once part of and the ligands stripped away by heating or photoly-
cluster, could recombine forming the original cluster. sis, leaving a bare, known nuclearity cluster on the sur-
This type of regeneration is most easily conceived for face. Unfortunately, almost all of these attempts have
binary metal carbonyl clusters. The unlikelihood that failed, with the possible exception of very stable, strongly
clusters containing (µ 3 -CPh) and (µ 4 -PPh) ligands could bound osmium clusters. In most cases the complete re-
be degraded and regenerated with no other Co-containing moval of ligands is difficult, and the deposited cluster is
compounds being formed argues for intact cluster rather more labile and fragile than was initially expected.
catalysis. The specific hydroformylation reactions these Nevertheless, this is an area for much successful future
clusters have been found to catalyze are the conversions work.
of 1- and 2-pentene to aldehydes. Under relatively mild Clearly there are many reasons for the continued inter-
reaction conditions (T = 90 −150 C) the yields were est in cluster compounds. Recall it was just 80 years ago
◦
excellent and the selectivity encouraging. Specifically, that [Ta 6 Cl 12 ] 2+ was synthesized. Over 40 years passed
the hydroformylation of 1-pentene at 110 Cgavea before the true nature of this compound was realized. In
◦
94% yield of the terminal 1-hexanal and the branched the 40 years that have followed the realization that metal
products 2-methylpentanal and 2-ethylpentanal. The ratio cluster compounds do exist great progress has been made
of normal to branched products was 4.7. in our understanding of these systems. However, for the
Another system in which intact cluster catalysis seems thousands of cluster compounds known today it is proba-
likely is the synthesis gas (CO/H 2 ) production of ethy- bly safe to say that only a small fraction of their reaction
lene glycol catalyzed by an anionic rhodium cluster of chemistry has been uncovered. With the persistent interest
uncertain or undisclosed identity. From high-temperature in these compounds many more thousands are sure to be