Page 208 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 208
190 Engineered interfaces in )fiber reinforced composites
Fig. 5.13. Schematic models for chemical reaction between oxidized carbon fiber surface and epoxy
matrix. After Hone et al. (1977).
contents (if nitric acid or ammonia is used as an oxidative medium) on the fiber
surface, in the form of carboxyl, hydroxyl, carbonyl and phenolic groups, as
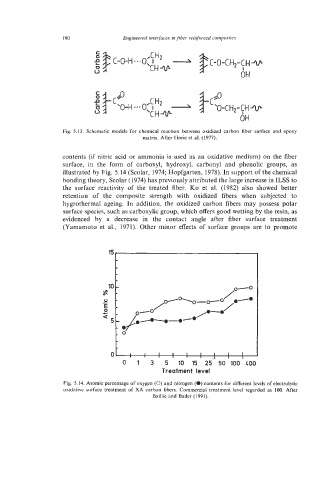
illustrated by Fig. 5.14 (Scolar, 1974; Hopfgarten, 1978). In support of the chemical
bonding theory, Scolar (1974) has previously attributed the large increase in ILSS to
the surface reactivity of the treated fiber. KO et al. (1982) also showed better
retention of the composite strength with oxidized fibers when subjected to
hygrothermal ageing. In addition, the oxidized carbon fibers may possess polar
surface species, such as carboxylic group, which offers good wetting by the resin, as
evidenced by a decrease in the contact angle after fiber surface treatment
(Yamamoto et al., 1971). Other minor effects of surface groups are to promote
10 -
s-
.- - t-J-o\o-o-o /O-O
0
E - / ,e--@
2 5 L -a /zZ-e-.-e /@-@
-0
0 I I I I I I J I 1 I
I
I