Page 213 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 213
Chapter 5. Surfuce treatments of fibers und effects on composite properties 195
Table 5.7
Summary of off-axis properties of carbon fiber-828 mPDA epoxy matrix composites with different fiber
surface treatmentsa
~
Off-axis properties AU-4 fiber AS-4 fiber AS4C fiber
Transverse tensile strength (MPa) 18.0 f 3.9 34.2 f 6.2 41.2 f 4.7
Transverse tensile modulus (GPa) 8.9 f 0.6 9.8 f 0.6 10.3 f 0.6
Transverse flexural strength (MPa) 21.4 f 5.8 50.2 f 3.4 75.6 f 14.0
Transverse flexural modulus (GPa) 10.2 f 1.5 9.9 f 0.5 10.7 f 0.6
[ i 4513, in-plane shear strength (MPa) 37.2 i 1.8 72.2 f 12.4 97.5 f 7.4
[ i 4513, in-plane shear modulus (GPa) 9.1 f 1.5 6.2 f 0.5 6.0 2 0.2
Iosipescu in-plane shear strength (MPa) 55.0 i 3.0 95.6 i 5.1 93.8 & 3.3
Iosipescu in-plane shear modulus (GPa) 7.2 i 0.5 6.4 i 1.0 7.9 f 0.4
Short beam interlaminar shear strength (MPa) 47.5 f 5.4 84.0 i 7.0 93.2 f 3.8
“After Drzal and Madhukar (1993).
improved interlaminar fracture toughness is the matrix deformation enhanced by
the strong interface bond. The improvement in fracture toughness from this source
seems to be larger than the loss arising from the brittle interphase material
surrounding the AS fiber. This observation has a practical implication in that for a
composite containing a very brittle resin, such as a highly cross-linked epoxy, the
interlaminar fracture toughness can be maximized by improving the interfacial bond
to a sufficiently high level.
The increase in mode I1 interlaminar fracture toughness is even more significant
than the mode I interlaminar fracture toughness. The similarity in the changes of
magnitude of the mode I1 fracture toughness and the ILSS with regard to the level of
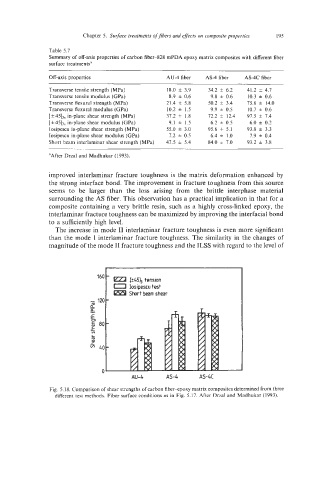
- 120 c ezl rt4513 tension
0 Iosittescu test
Short beam shear
.m
AU-4 AS4 AS4
Fig. 5.18. Comparison of shcar strengths of carbon fiber-epoxy matrix composites determined from three
different test methods. Fibcr surfacc conditions as in Fig. 5.17. After Drzal and Madhukar (1993).