Page 212 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 212
I94 Engineered interfaces in fiber reinforced composites
compression
0 Tension T
AU-4 AS-4 AS-4C
200
- 150
B
-
L7
-
3
Lo
3
-g 100
-
E
m
c
._
U
3
50
c
0
1
0
(b) AU-4 AS-4 AS-4C
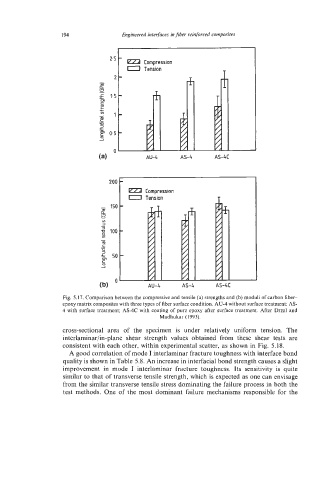
Fig. 5.17. Comparison between the compressive and tensile (a) strengths and (b) moduli of carbon fiber-
epoxy matrix composites with three types of fiber surface condition. AU-4 without surface treatment; AS-
4 with surface treatment; AS-4C with coating of pure epoxy after surface treatment. After Drzal and
Madhukar (1993).
cross-sectional area of the specimen is under relatively uniform tension. The
interlaminar/in-plane shear strength values obtained from these shear tests are
consistent with each other, within experimental scatter, as shown in Fig. 5.18.
A good correlation of mode I interlaminar fracture toughness with interface bond
quality is shown in Table 5.8. An increase in interfacial bond strength causes a slight
improvement in mode I interlaminar fracture toughncss. Its sensitivity is quite
similar to that of transverse tensile strength, which is expected as one can envisage
from the similar transverse tensile stress dominating the failure process in both the
test methods. One of the most dominant failure mechanisms responsible for the