Page 269 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 269
250 Engineered interfaces in fiber reinforced composites
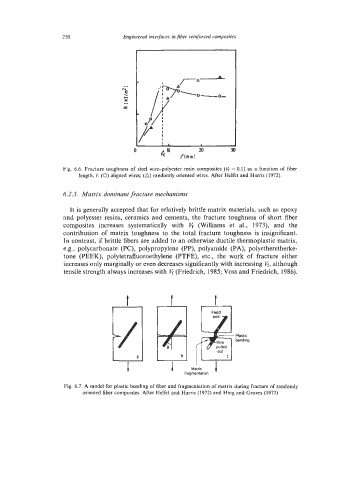
0 20 3
Fig. 6.6. Fracture toughness of steel wirepolyester resin composites (6 = 0.1) as a function of fiber
length, l? (0) aligned wires; (A) randomly oriented wires. After Helfet and Hams (1972).
6.2.3. Matrix dominant fracture mechanisms
It is generally accepted that for relatively brittle matrix materials, such as epoxy
and polyester resins, ceramics and cements, the fracture toughness of short fiber
composites increases systematically with vf (Williams et al., 1973), and the
contribution of matrix toughness to the total fracture toughness is insignificant.
In contrast, if brittle fibers are added to an otherwise ductile thermoplastic matrix,
e.g., polycarbonate (PC), polypropylene (PP), polyamide (PA), polyetheretherke-
tone (PEEK), polytetrafluoroethylene (F’TFE), etc., the work of fracture either
increases only marginally or even decreases significantly with increasing fi, although
tensile strength always increases with vf (Friedrich, 1985; Voss and Friedrich, 1986).
Fixed
Plastic
bending
pulled
i. R I
I
1 i Matrix 1
fragmentation
Fig. 6.7. A model for plastic bending of fiber and fragmentation of matrix during fracture of randomly
oriented fiber composites. After Helfet and Harris (1972) and Hing and Groves (1972).